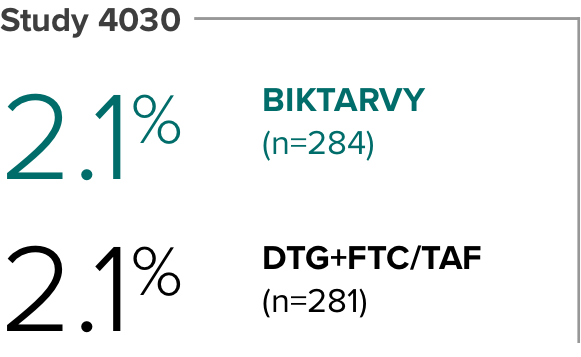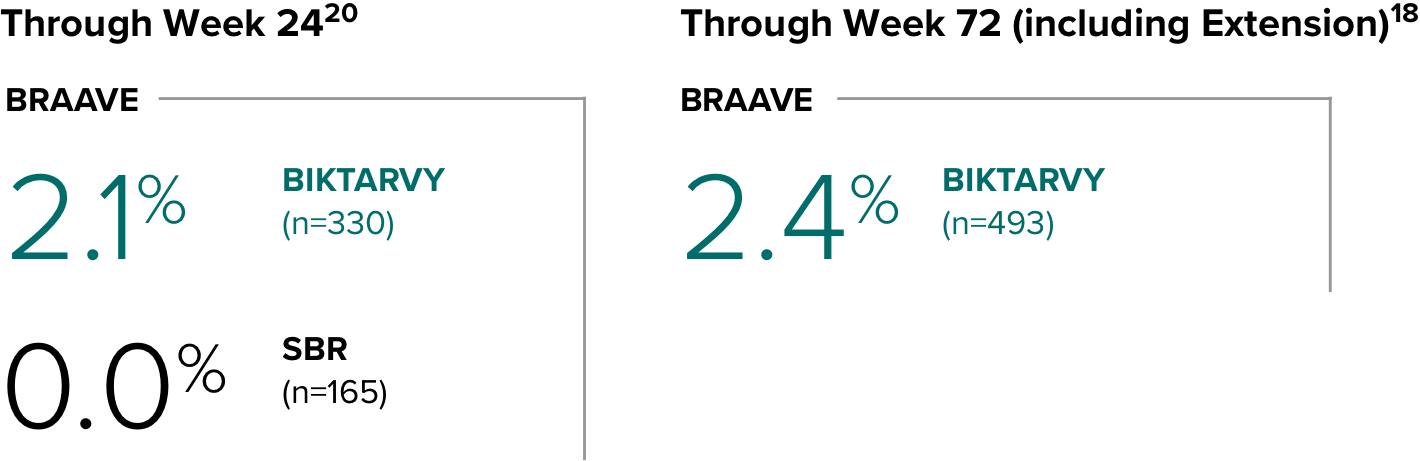6
Adverse Reactions & Discontinuations
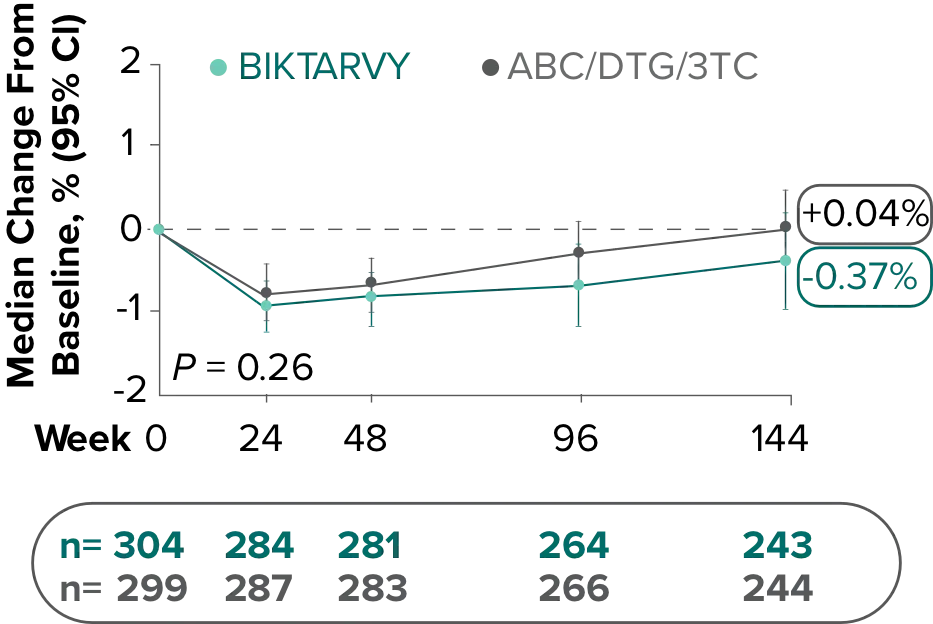
Weight change through Week 144
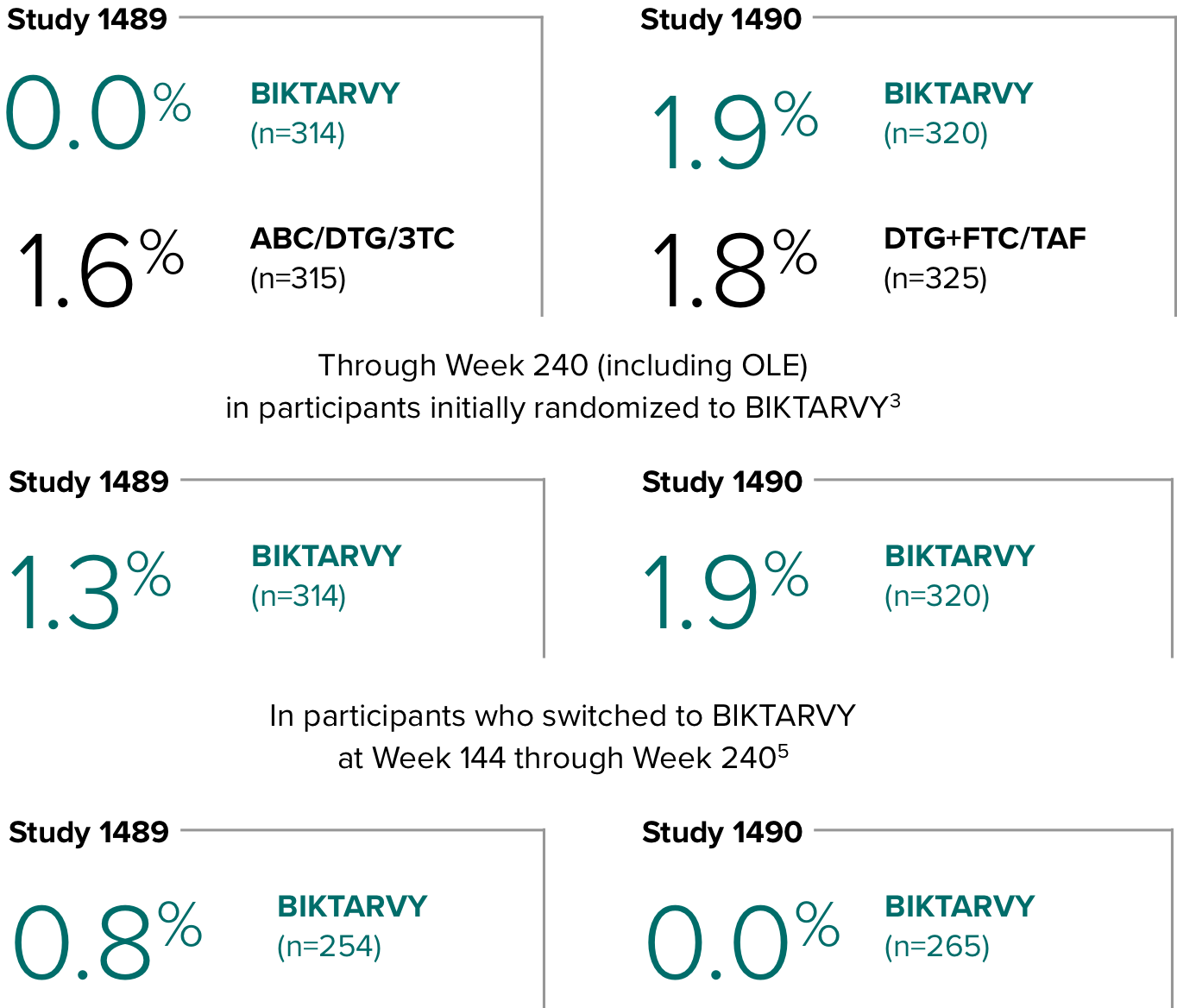
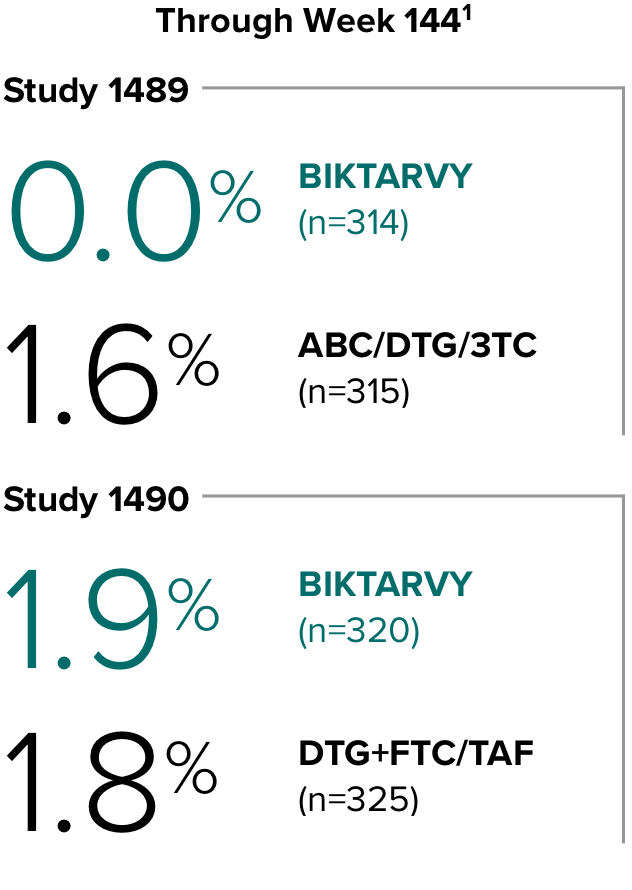
Study 14891,2
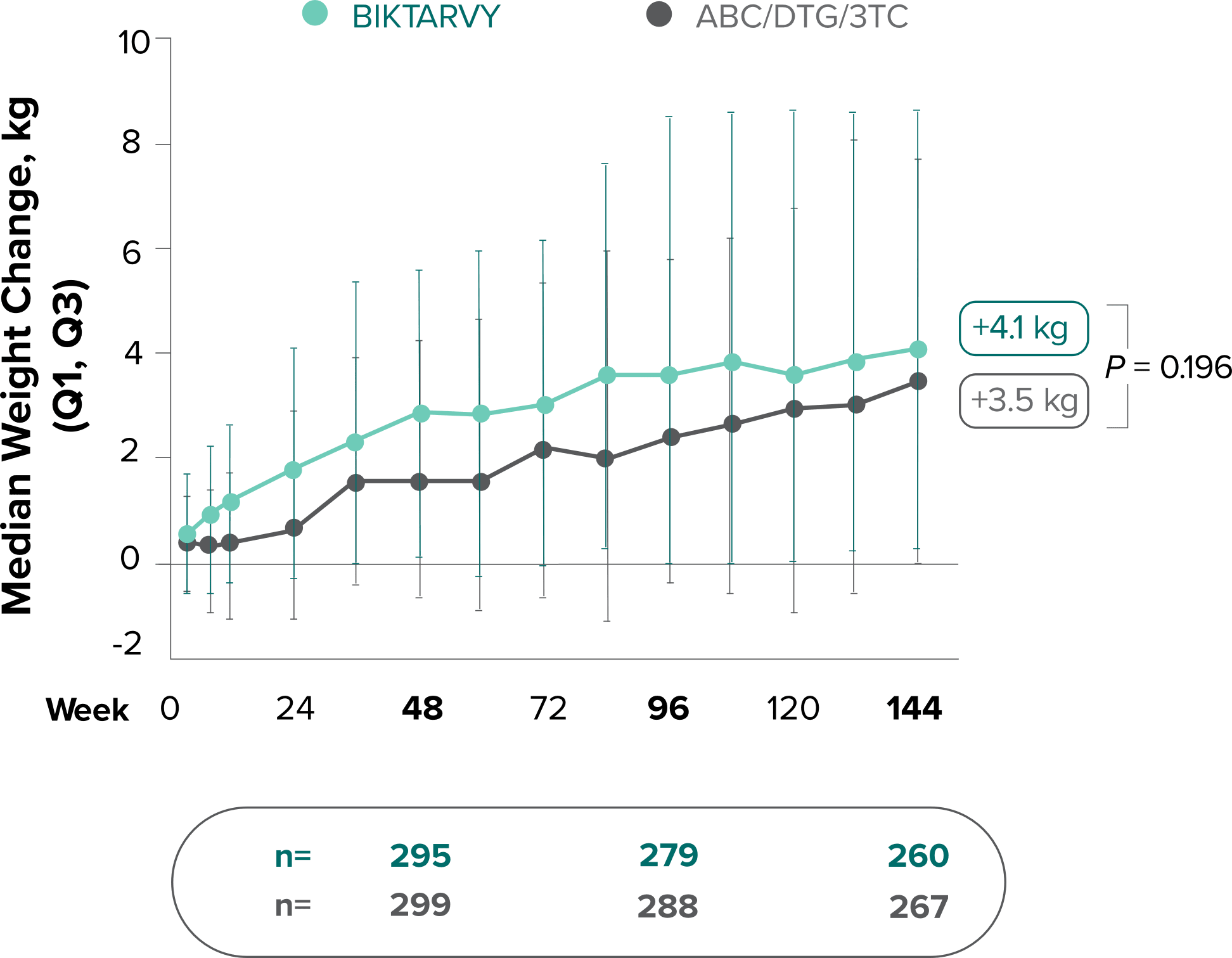
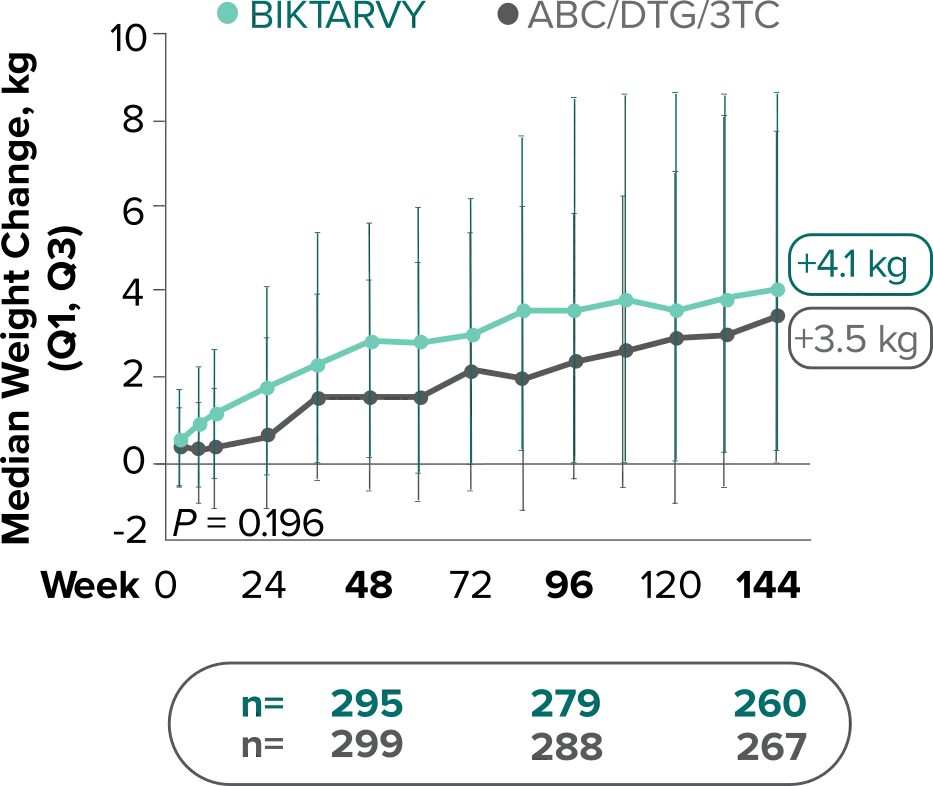
In Study 1489, no adults discontinued BIKTARVY due to weight-related AEs through Week 1441,2
- In Study 1489, an AE of weight increase was reported for BIKTARVY (2.9%), ABC/DTG/3TC (4.1%), and weight decrease for BIKTARVY (1.9%), ABC/DTG/3TC (1.6%)2
Study 14901,2
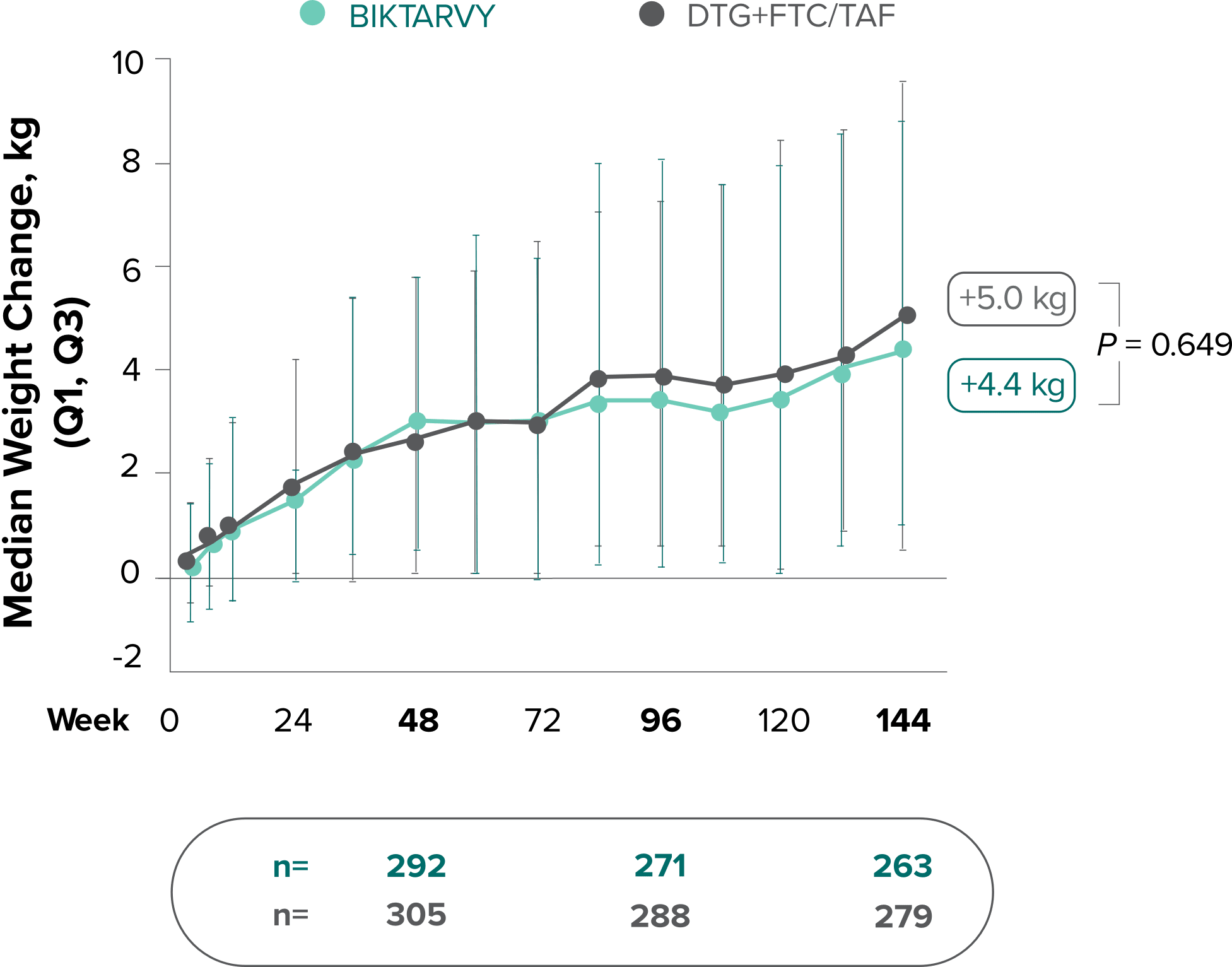
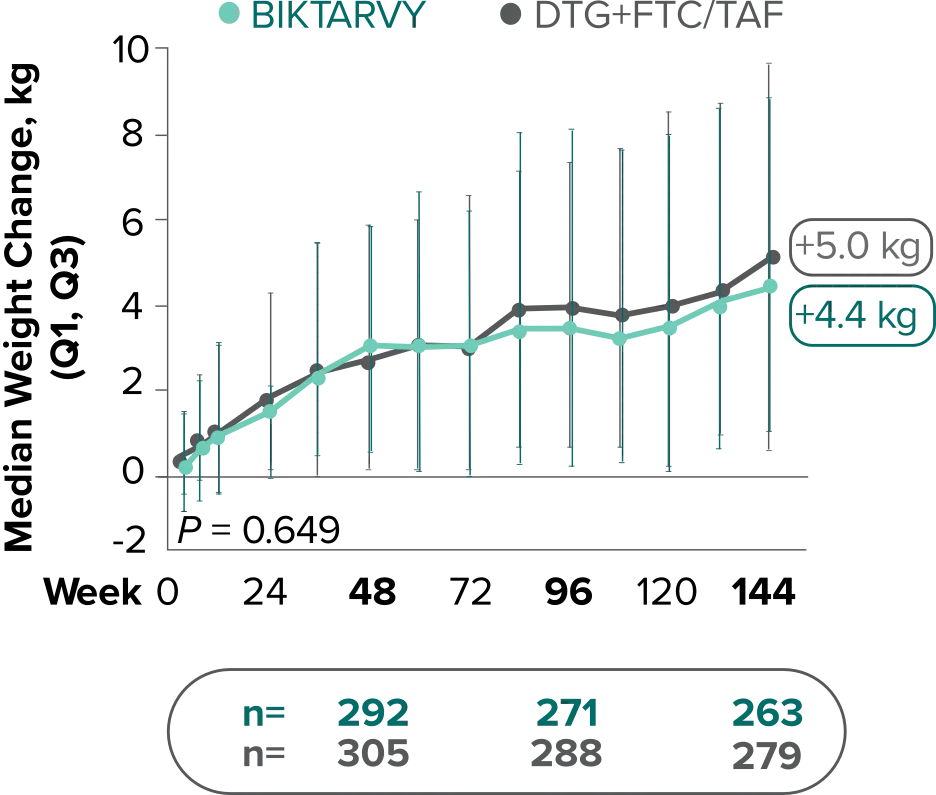
In Study 1490, no adults discontinued BIKTARVY due to weight-related AEs through Week 1441,2
- In Study 1490, an AE of weight increase was reported for BIKTARVY (2.5%), DTG+FTC/TAF (3.1%), and weight decrease for BIKTARVY (0.9%), DTG+FTC/TAF (0.9%)2
Weight change through Week 2403-5
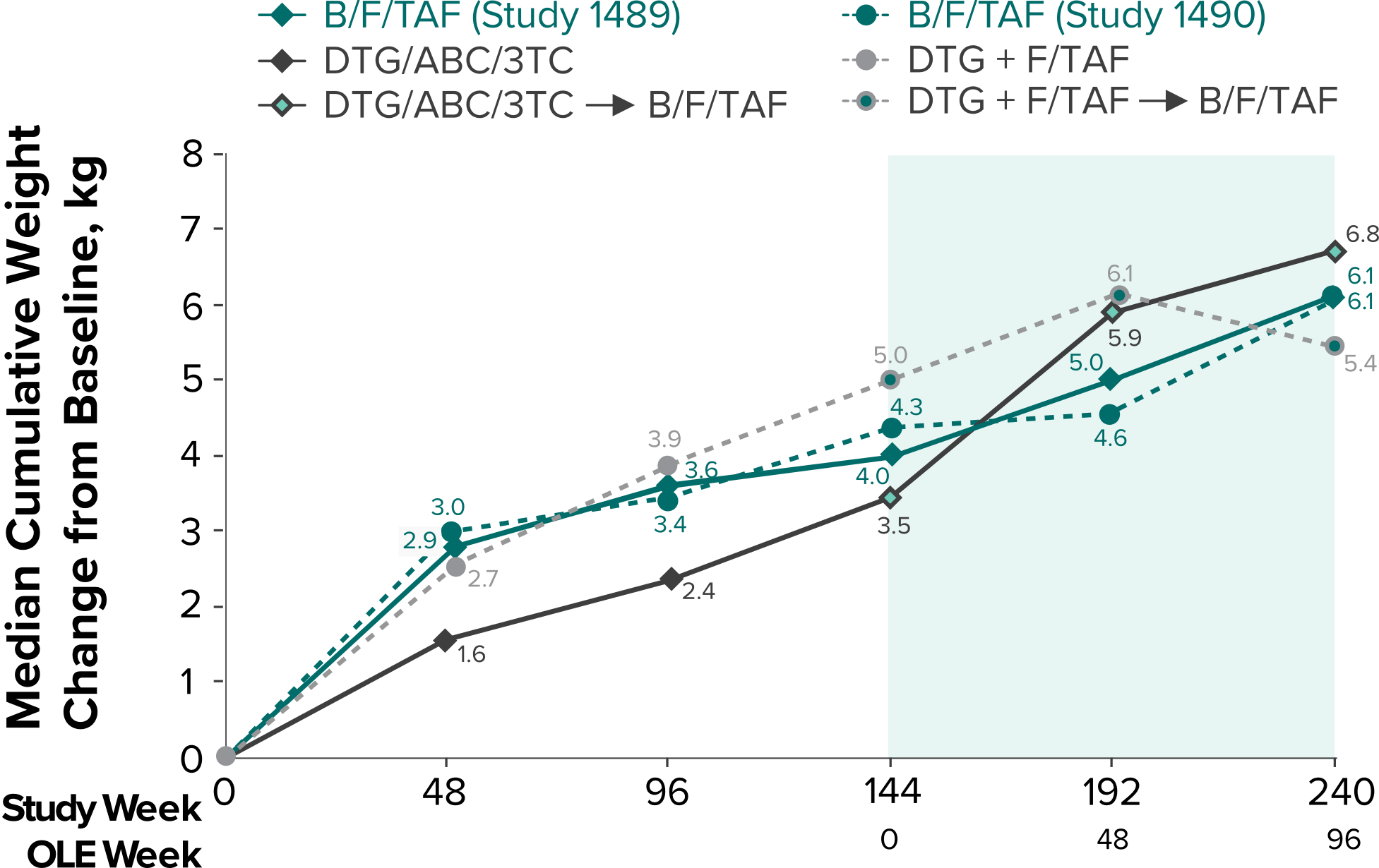
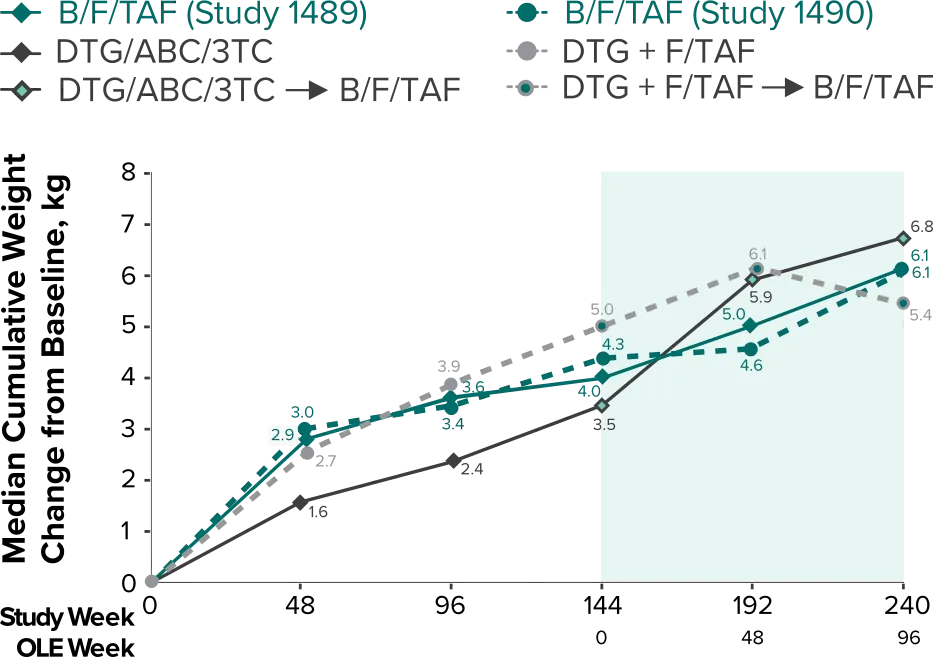
- In the OLE through Week 240, 2 study participants discontinued due to a weight-related adverse event attributed to study drug.3-5
- Median cumulative weight gain from baseline to Week 240, including the OLE, was 6.1 kg for participants initially randomized to BIKTARVY3
- Cumulative median weight changes at Week 240 were numerically similar for all treatment groups4
- At Week 144, significantly lower median weight changes were observed in participants treated with DTG/ABC/3TC vs DTG+FTC/TAF: 3.5 kg vs 5.0 kg (P = 0.025)4,5
- In the OLE from Week 144 to Week 240, greater median weight changes were observed in participants who switched to BIKTARVY from DTG/ABC/3TC vs those who switched from DTG+FTC/TAF: 2.4 kg vs 1.3 kg (P = 0.01)4,5
3TC, lamivudine; ABC, abacavir; AE, adverse event; DTG, dolutegravir; FTC, emtricitabine; OLE, open-label extension; TAF, tenofovir alafenamide.
References:
- Orkin C, DeJesus E, Sax PE, et al. Fixed-dose combination bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide versus dolutegravir-containing regimens for initial treatment of HIV-1 infection: week 144 results from two randomised, double-blind, multicentre, Phase 3, non-inferiority trials. Lancet HIV. 2020;7(6):e389-e400.
- Data on file. Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Wohl DA, Pozniak A, Workowski K, et al. B/F/TAF five-year outcomes in treatment-naïve adults. Poster presented at: Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; February 12-16, 2022; Virtual. Poster 494.
- Orkin C, Antinori A, Rockstroh J, et al. Outcomes after switching from 144 weeks of blinded DTG/ABC/3TC or DTG+F/TAF to 96 weeks of open-label B/F/TAF. Poster presented at: HIV Glasgow 2022; October 23-26, 2022; Glasgow UK. Poster P088.
- Orkin C, Antinori A, Rockstroh J, et al. Switch to bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide from dolutegravir-based therapy. AIDS. 2024;38:983-991.
Study 1489: Changes in hip BMD through Week 1441
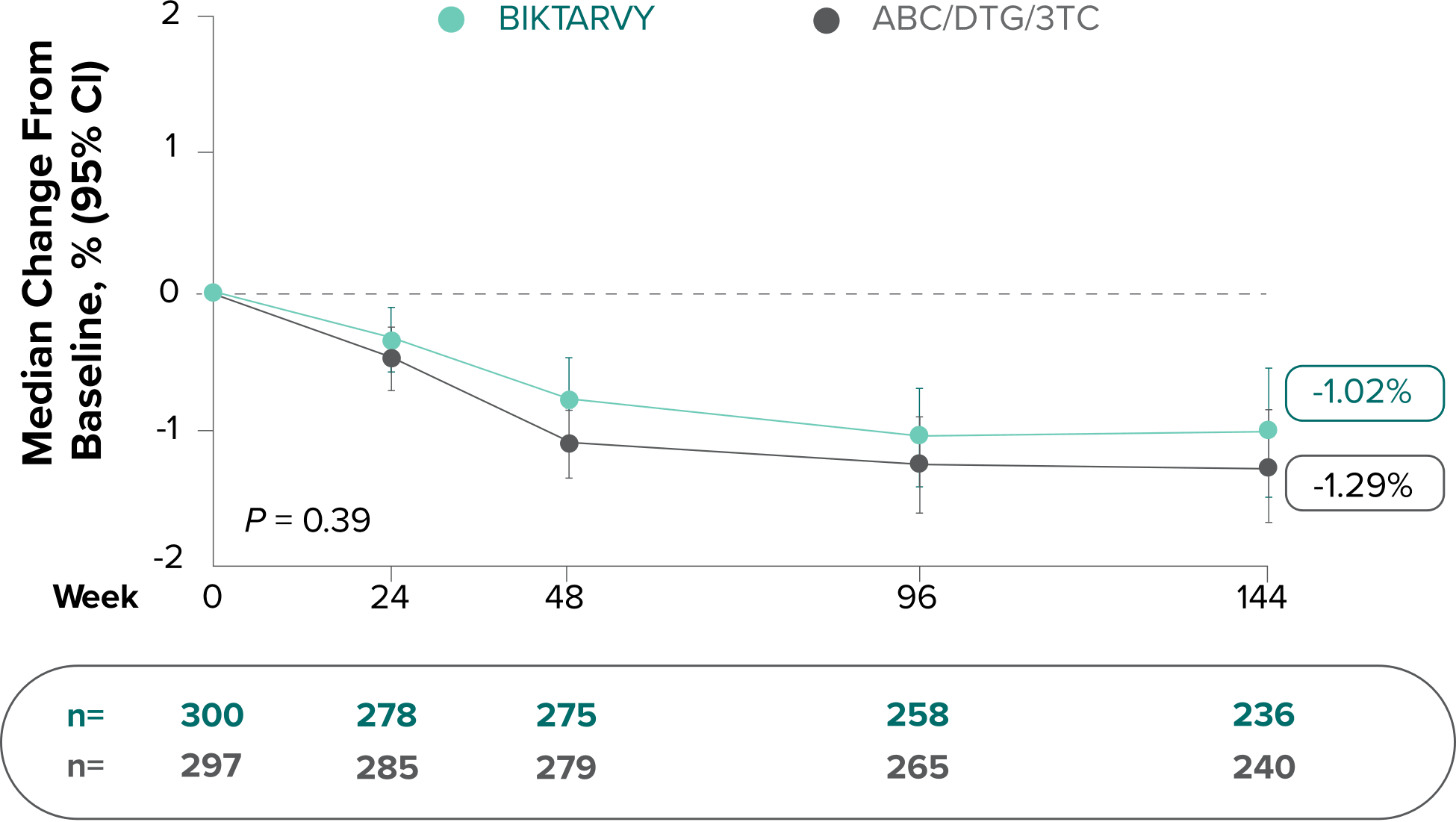
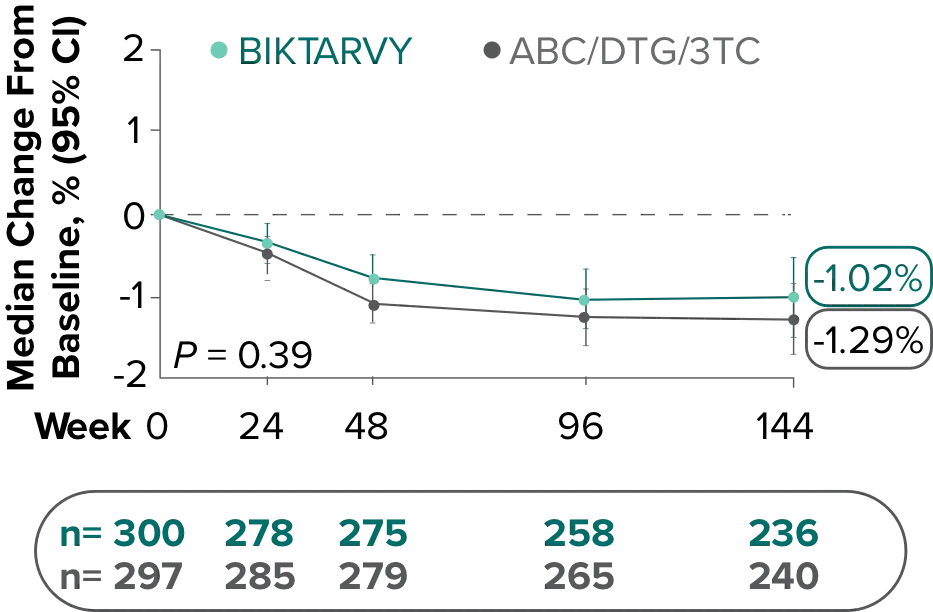
- BMD declines of ≥7% at the total hip were experienced in 1% of BIKTARVY participants and 2% of ABC/DTG/3TC participants at Week 48, in 2% of BIKTARVY participants and 3% of ABC/DTG/3TC participants at Week 96, and in 5% of BIKTARVY participants and 4% of ABC/DTG/3TC participants at Week 1442
- – Analysis was conducted in a subset of the study population (n=597)2
In the OLE:
- A mean change of −0.3% was observed from baseline at Week 240 (n=197)3
- BMD declines of ≥7% at the total hip were experienced in 8% of participants (n=15/197) at Week 2402
- Includes only participants initially randomized to BIKTARVY at Week 0, as these participants took BIKTARVY for 240 weeks3
The long-term clinical significance of changes in BMD is not known.
- BMD was assessed at baseline, Week 24, Week 48, Week 96, Week 144, Week 192, and Week 240 by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans2,3
Study 1489: Changes in lumbar spine BMD through Week 1441
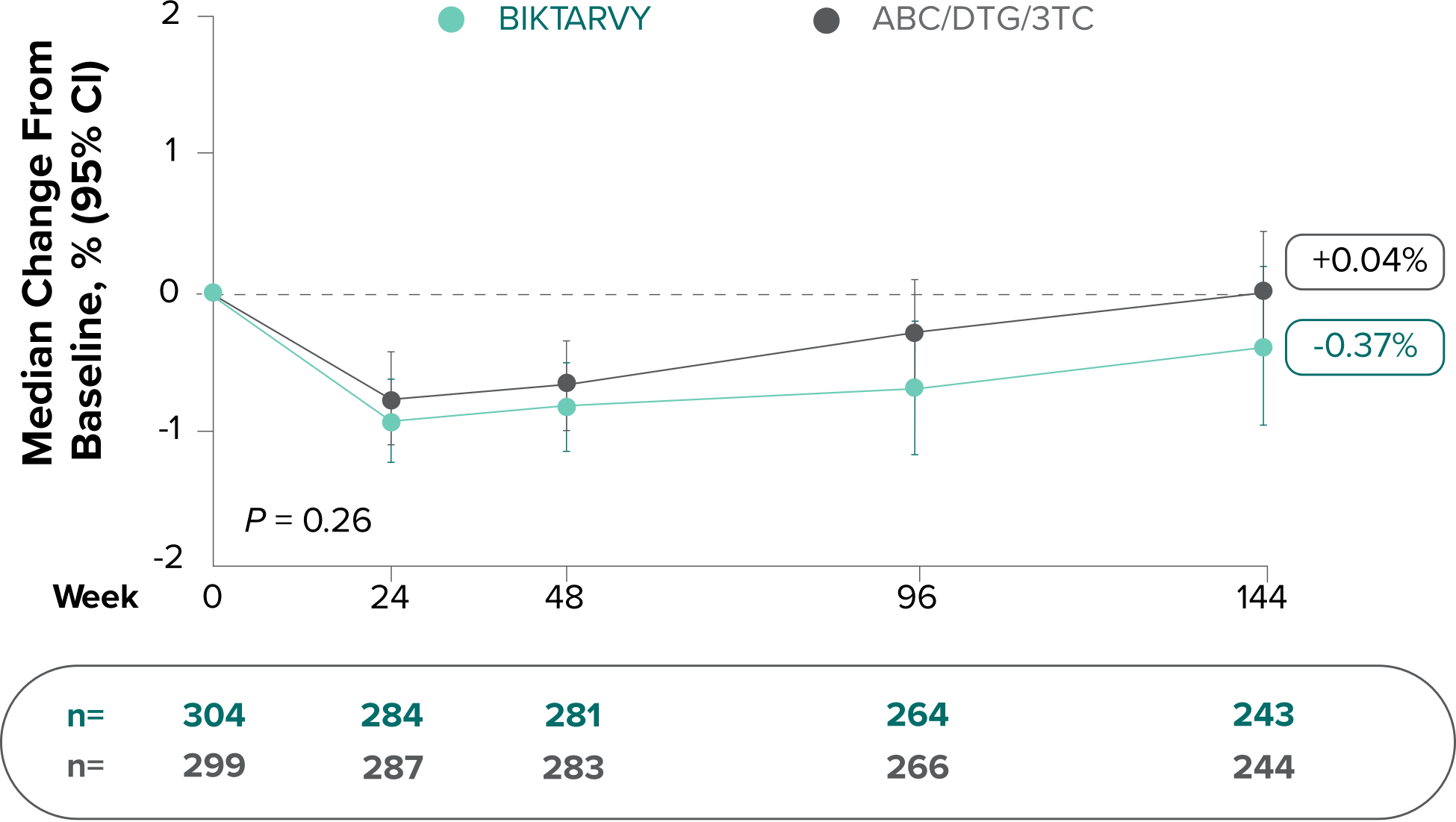
- BMD declines of ≥5% at the lumbar spine were experienced in 11% of BIKTARVY participants and 6% of ABC/DTG/3TC participants at Week 48, in 12% of BIKTARVY participants and 6% of ABC/DTG/3TC participants at Week 96, and in 13% of BIKTARVY participants and 8% of ABC/DTG/3TC participants at Week 1442
- – Analysis was conducted in a subset of the study population (n=603)2
In the OLE:
- A mean change of −0.2% was observed from baseline at Week 240 (n=201)3
- BMD declines of ≥5% at the lumbar spine were experienced in 20% of participants (n=41/201) at Week 2402
- Includes only participants initially randomized to BIKTARVY at Week 0, as these participants took BIKTARVY for 240 weeks3
The long-term clinical significance of changes in BMD is not known.
- BMD was assessed at baseline, Week 24, Week 48, Week 96, Week 144, Week 192, and Week 240 by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans2,3
BMD was measured only in Study 1489
BMD, bone mineral density; CI, confidence interval; FTC, emtricitabine; OLE, open-label extension.
References:
- Orkin C, DeJesus E, Sax PE, et al. Fixed-dose combination bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide versus dolutegravir-containing regimens for initial treatment of HIV-1 infection: week 144 results from two randomised, double-blind, multicentre, Phase 3, non-inferiority trials. Lancet HIV. 2020;7(6):e389-e400.
- Data on file. Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Wohl DA, Pozniak A, Workowski K, et al. B/F/TAF five-year outcomes in treatment-naïve adults. Poster presented at: Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; February 12-16, 2022; Virtual. Poster 494.
Changes in eGFRCG and serum creatinine through Week 144
Study 14891-3
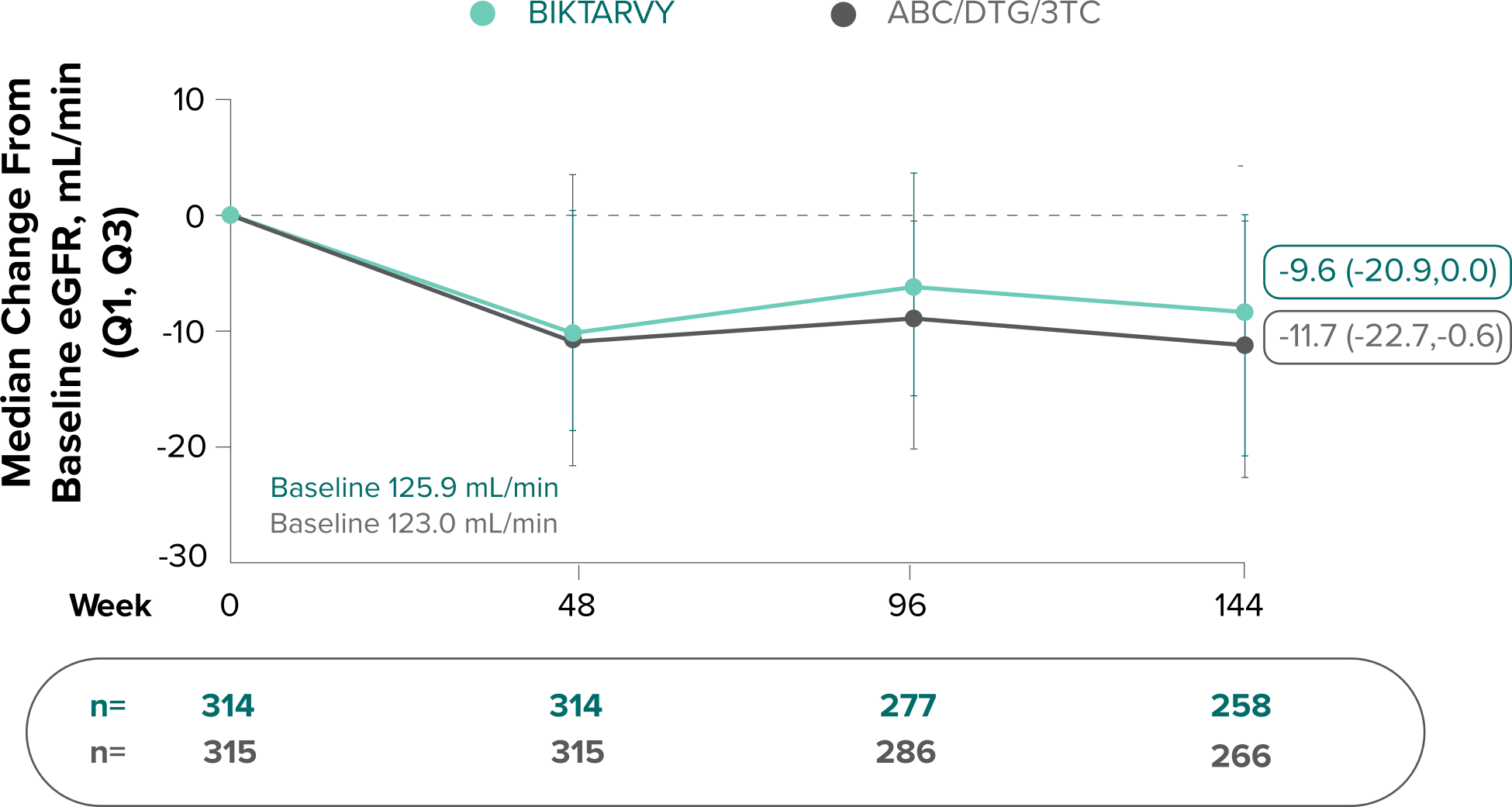
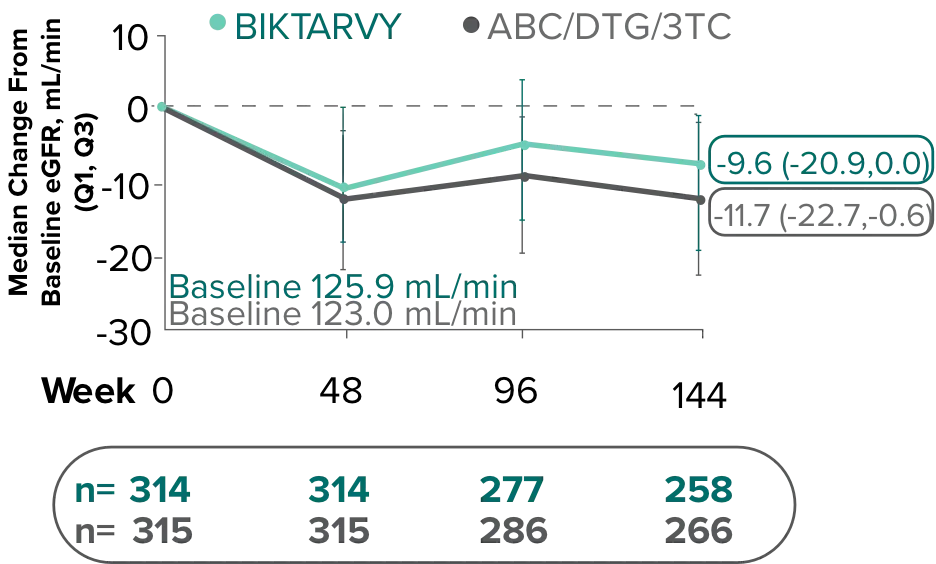
- Median serum creatinine increased by 0.1 mg/dL in the BIKTARVY arm and by 0.11 mg/dL in the ABC/DTG/3TC arm from baseline1
In the OLE for Study 1489 in participants who were initially randomized to BIKTARVY at Week 0 and continued through Week 240:
- A median eGFR change of −8.2 mL/min from baseline was observed at Week 240 (n=213)4,5
- Median serum creatinine increased by 0.11 mg/dL in participants from baseline through Week 2405
In participants who switched from ABC/DTG/3TC to BIKTARVY at Week 144 through Week 240:
- A median eGFR change of +2.0 mL/min from Week 144 was observed at Week 240 (n=217)6
The long-term clinical significance of changes in eGFR is not known.
Study 14901,7,8
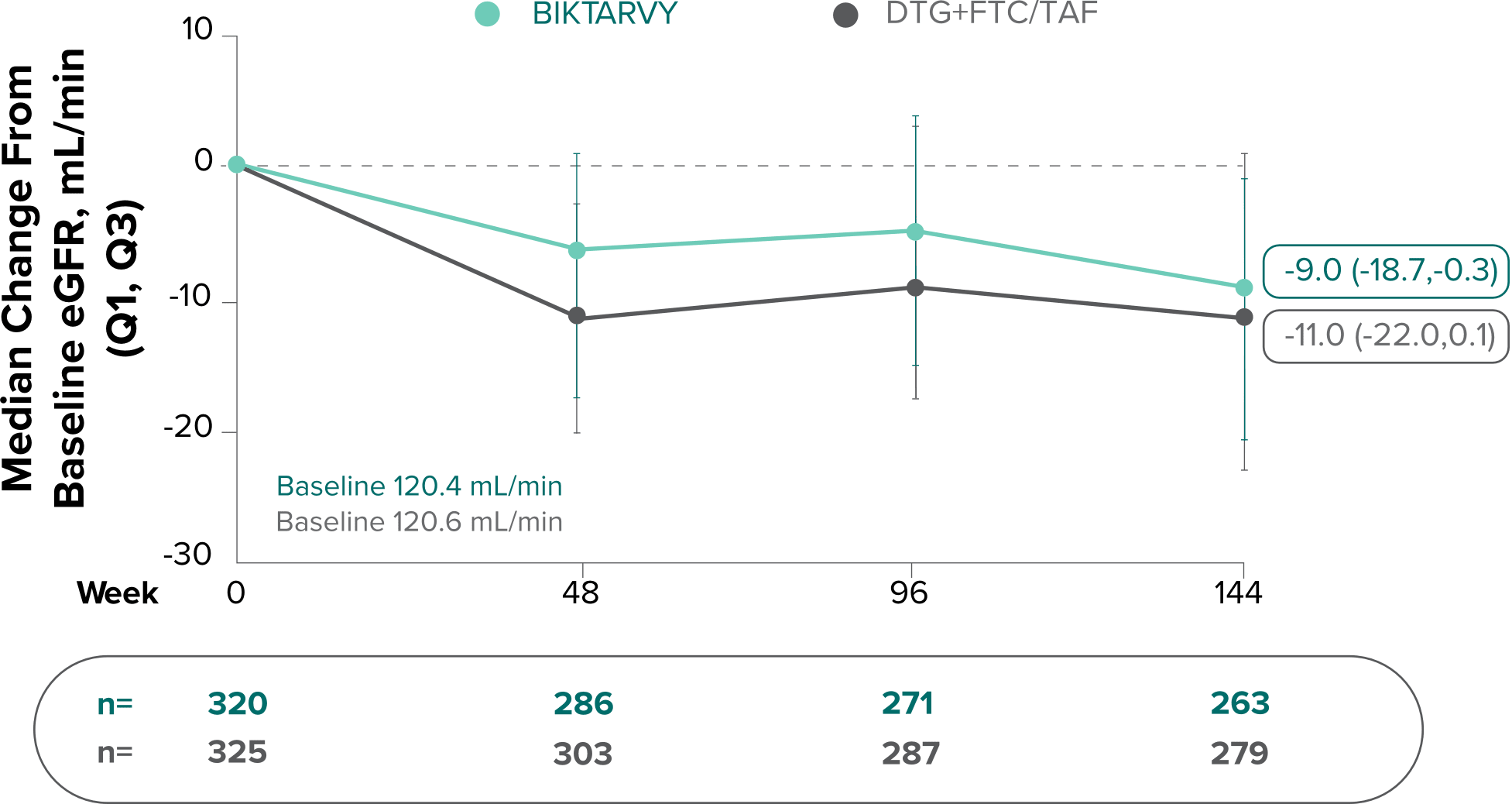
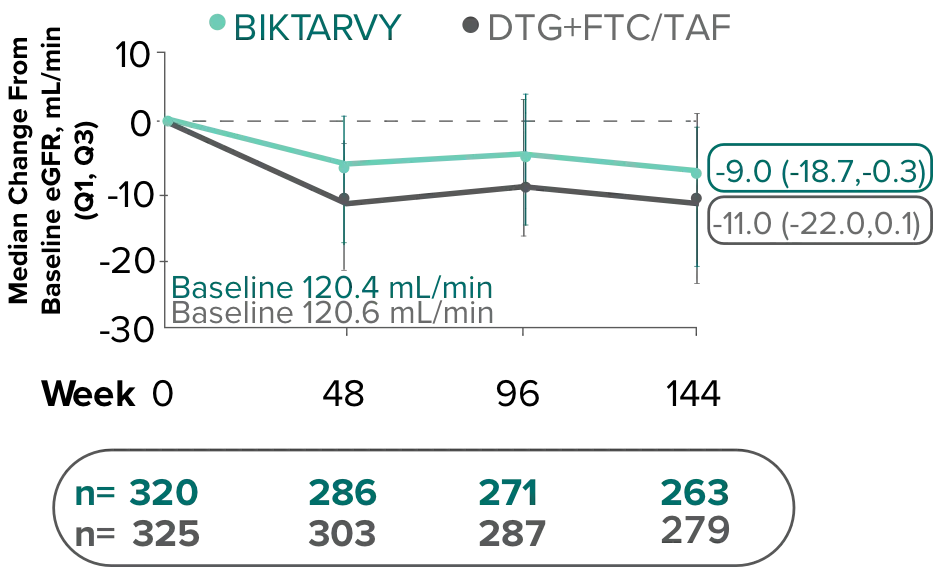
- Median serum creatinine increased by 0.11 mg/dL in the BIKTARVY arm and by 0.12 mg/dL in the DTG+FTC/TAF arm from baseline1
In the OLE for Study 1490 in participants who were initially randomized to BIKTARVY at Week 0 and continued through Week 240:
- A median eGFR change of -8.5 mL/min from baseline was observed at Week 240 (n=217)4,5
- Median serum creatinine increased by 0.11 mg/dL in patients from baseline through Week 2405
In participants who switched from DTG+FTC/TAF to BIKTARVY at Week 144 through Week 240:
- A median eGFR change of +1.3 mL/min from Week 144 was observed at Week 240 (n=233)6
The long-term clinical significance of changes in eGFR is not known.
3TC, lamivudine; ABC, abacavir; DTG, dolutegravir; eGFRCG, estimated glomerular filtration rate (Cockcroft-Gault); FTC, emtricitabine; OLE, open-label extension; TAF, tenofovir alafenamide.
References:
- Orkin C, DeJesus E, Sax PE, et al. Fixed-dose combination bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide versus dolutegravir-containing regimens for initial treatment of HIV-1 infection: week 144 results from two randomised, double-blind, multicentre, Phase 3, non-inferiority trials. Lancet HIV. 2020;7(6):e389-e400.
- Wohl DA, Yazdanpanah Y, Baumgarten A, et al. Bictegravir combined with emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide versus dolutegravir, abacavir, and lamivudine for initial treatment of HIV-1 infection: week 96 results from a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, Phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet HIV. 2019;6(6):e355-e363.
- Gallant J, Lazzarin A, Mills A, et al. Bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide versus dolutegravir, abacavir, and lamivudine for initial treatment of HIV-1 infection (GS-US-380-1489): a double-blind, multicentre, Phase 3, randomised controlled non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2017;390(10107):2063-2072.
- Wohl DA, Pozniak A, Workowski K, et al. B/F/TAF five-year outcomes in treatment-naïve adults. Poster presented at: Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; February 12-16, 2022; Virtual. Poster 494.
- Data on file. Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Orkin C, Antinori A, Rockstroh J, et al. Outcomes after switching from 144 weeks of blinded DTG/ABC/3TC or DTG+F/TAF to 96 weeks of open-label B/F/TAF. Poster presented at: HIV Glasgow 2022; October 23-26, 2022; Glasgow UK. Poster P088.
- Sax PE, Pozniak A, Montes ML, et al. Coformulated bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide versus dolutegravir with emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide, for initial treatment of HIV-1 infection (GS-US-380-1490): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, Phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2017;390(10107):2073-2082.
- Stellbrink H-J, Arribas JR, Stephens JL, et al. Co-formulated bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide versus dolutegravir with emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide for initial treatment of HIV-1 infection: week 96 results from a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, Phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet HIV. 2019;6(6):e364-e372.
Median change in fasting lipids from baseline through Week 144
Study 14891
BIKTARVY
Baseline:
(n=305)
Week 144:
(n=247)
ABC/
DTG/3TC
Baseline:
(n=305)
Week 144:
(n=256*)
+14
+10
+21
+14
+5
+6
+6
+5
-0.1
-0.3
Study 14901
Study 14901
BIKTARVY
Baseline:
(n=314)
Week 144:
(n=256)
DTG+
FTC/TAF
Baseline:
(n=321)
Week 144:
(n=274)
+12
+12
+19
+19
+3
+5
+2
+2
0.0
-0.1
*Except for triglycerides, which are (n=255) at Week 144.
In the OLE for Study 1489:
- In participants who were initially randomized to BIKTARVY at Week 0 and continued through Week 240, median changes in fasting lipids from baseline were as follows (n=202): Total-C: +20 mg/dL, LDL-C: +22 mg/dL, HDL-C: +5 mg/dL, Triglycerides: +11 mg/dL, Total-C:HDL-C ratio: 0.02
- In participants who switched from ABC/DTG/3TC to BIKTARVY at Week 144 through Week 240, median changes in fasting lipids from baseline were as follows (n=215)†: Total-C: +7 mg/dL, LDL-C: +2 mg/dL, HDL-C: 0.0 mg/dL, Triglycerides: -3 mg/dL, Total-C:HDL-C ratio: +0.12
†Except for triglycerides, which are (n=213) at Week 240.
In the OLE for Study 1490:
- In participants who were initially randomized to BIKTARVY at Week 0 and continued through Week 240, median changes in fasting lipids from baseline were as follows (n=208): Total-C: +22 mg/dL, LDL-C: +17 mg/dL, HDL-C: +4 mg/dL, Triglycerides: +10 mg/dL, Total-C:HDL-C ratio: +0.12
- In participants who switched from DTG+FTC/TAF to BIKTARVY at Week 144 through Week 240, median changes in fasting lipids from baseline were as follows (n=225): Total-C: +5 mg/dL, LDL-C: -2 mg/dL, HDL-C: +1 mg/dL, Triglycerides: +2 mg/dL, Total-C:HDL-C ratio: -0.12
Lab abnormalities were observed with both BIKTARVY and comparators through Week 144
Study 14891,3
Reported in ≥2% (Grades
3-4) of Treatment-Naïve
Adults Who Received
BIKTARVY
BIKTARVY
(n=314)
ABC/
DTG/
3TC
(n=315)
3%
4%
2%
2%
5%
3%
8%
8%
3%
4%
5%
5%
2%
2%
2%
2%
Study 14901,3
Study 14901,3
BIKTARVY
(n=320)
DTG+
FTC/TAF
(n=325)
3%
4%
3%
1%
2%
3%
6%
4%
3%
4%
4%
6%
<1%
2%
1%
1%
Lab abnormalities through Week 240
Study 14892
Study 14902
Reported in ≥2% (Grades 3-4) of Treatment-Naïve Adults Initially Randomized at Week 0 and Continued Through Week 240
BIKTARVY(n=314)
BIKTARVY(n=320)
Amylase (increased)
4%
4%
ALT (increased)
3%
4%
AST (increased)
5%
3%
Creatine kinase (increased)
12%
10%
Lipase (increased)‡
20%
3%
Neutrophils (decreased)
3%
4%
Serum glucose (fasting, hyperglycemia)
1%
3%
Total cholesterol (fasting, hypercholesterolemia)
2%
2%
LDL cholesterol (fasting, increased)
6%
5%
Urine glucose (glycosuria)
1%
2%
Urine RBC (hematuria, quantitative or dipstick)
2%
3%
Study 14892
Reported in ≥2% (Grades 3-4) of Treatment-Naïve Adults Initially Randomized at Week 0 and Continued Through Week 240
BIKTARVY(n=314)
Amylase (increased)
4%
ALT (increased)
3%
AST (increased)
5%
AST (increased)
5%
Creatine kinase (increased)
12%
Lipase (increased)‡
20%
Neutrophils (decreased)
3%
Serum glucose (fasting, hyperglycemia)
1%
Total cholesterol (fasting, hypercholesterolemia)
2%
LDL cholesterol (fasting, increased)
6%
Urine glucose (glycosuria)
1%
Urine RBC (hematuria, quantitative or dipstick)
2%
Study 14902
Reported in ≥2% (Grades 3-4) of Treatment-Naïve Adults Initially Randomized at Week 0 and Continued Through Week 240
BIKTARVY(n=320)
Amylase (increased)
4%
ALT (increased)
4%
AST (increased)
3%
Creatine kinase (increased)
10%
Lipase (increased)‡
3%
Neutrophils (decreased)
4%
Serum glucose (fasting, hyperglycemia)
3%
Serum glucose (nonfasting, hyperglycemia)
2%
Total cholesterol (fasting, hypercholesterolemia)
2%
LDL cholesterol (fasting, increased)
5%
Urine glucose (glycosuria)
2%
Urine RBC (hematuria, quantitative or dipstick)
3%
Study 14892,4,5
Study 14902,4,5
Reported in ≥2% (Grades 3-4) of Adults Switched to BIKTARVY at Week 144 Through Week 240
ABC/DTG/3TC switched to BIKTARVY(n=254)
DTG+FTC/TAF switched to BIKTARVY(n=265)
Amylase (increased)
2%
2%
ALT (increased)
1%
2%
AST (increased)
2%
1%
Creatine kinase (increased)
4%
3%
Lipase (increased)‡
11%
21%
Serum glucose (fasting, hyperglycemia)
1%
2%
Serum glucose (nonfasting, hyperglycemia)
1%
3%
LDL-cholesterol (fasting, increased)
1%
3%
Triglycerides (increased)
2%
<1%
Urine glucose (glycosuria)
1%
3%
Study 14892,4,5
Reported in ≥2% (Grades 3-4) of Adults Switched to BIKTARVY at Week 144 Through Week 240
ABC/DTG/
3TC switched to BIKTARVY(n=254)
Amylase (increased)
2%
ALT (increased)
1%
AST (increased)
2%
Creatine kinase (increased)
4%
Lipase (increased)‡
11%
Serum glucose (fasting, hyperglycemia)
1%
Serum glucose (nonfasting, hyperglycemia)
1%
LDL cholesterol (fasting, increased)
1%
Triglycerides (increased)
2%
Urine glucose (glycosuria)
1%
Study 14902,4,5
Reported in ≥2% (Grades 3-4) of Adults Switched to BIKTARVY at Week 144 Through Week 240
DTG+
FTC/TAF switched to BIKTARVY(n=265)
Amylase (increased)
2%
ALT (increased)
2%
AST (increased)
1%
Creatine kinase (increased)
3%
Lipase (increased)‡
21%
Serum glucose (fasting, hyperglycemia)
2%
Serum glucose (nonfasting, hyperglycemia)
3%
LDL cholesterol (fasting, increased)
3%
Triglycerides (increased)
<1%
Urine glucose (glycosuria)
3%
‡Lipase test performed only in participants with serum amylase > 1.5 x ULN.
BIKTARVY is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). For patients weighing ≥25 kg, BIKTARVY is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (estimated CrCl <30 mL/min) except in virologically suppressed patients with CrCl <15 mL/min on chronic hemodialysis. BIKTARVY is not recommended for patients weighing ≥14 kg to <25 kg with CrCl <30 mL/min.
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CrCl, creatinine clearance; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; OLE, open-label extension; ULN, upper limit of normal.
References:
- Orkin C, DeJesus E, Sax PE, et al. Fixed-dose combination bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide versus dolutegravir-containing regimens for initial treatment of HIV-1 infection: week 144 results from two randomised, double-blind, multicentre, Phase 3, non-inferiority trials. Lancet HIV. 2020;7(6):e389-e400.
- Data on file. Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- BIKTARVY. Prescribing information. Gilead Sciences, Inc.; 2025.
- Orkin C, Antinori A, Rockstroh J, et al. Outcomes after switching from 144 weeks of blinded DTG/ABC/3TC or DTG+F/TAF to 96 weeks of open-label B/F/TAF. Poster presented at: HIV Glasgow 2022; October 23-26, 2022; Glasgow UK. Poster P088.
- Orkin C, Antinori A, Rockstroh J, et al. Switch to bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide from dolutegravir-based therapy. AIDS. 2024;38(suppl):983-991.
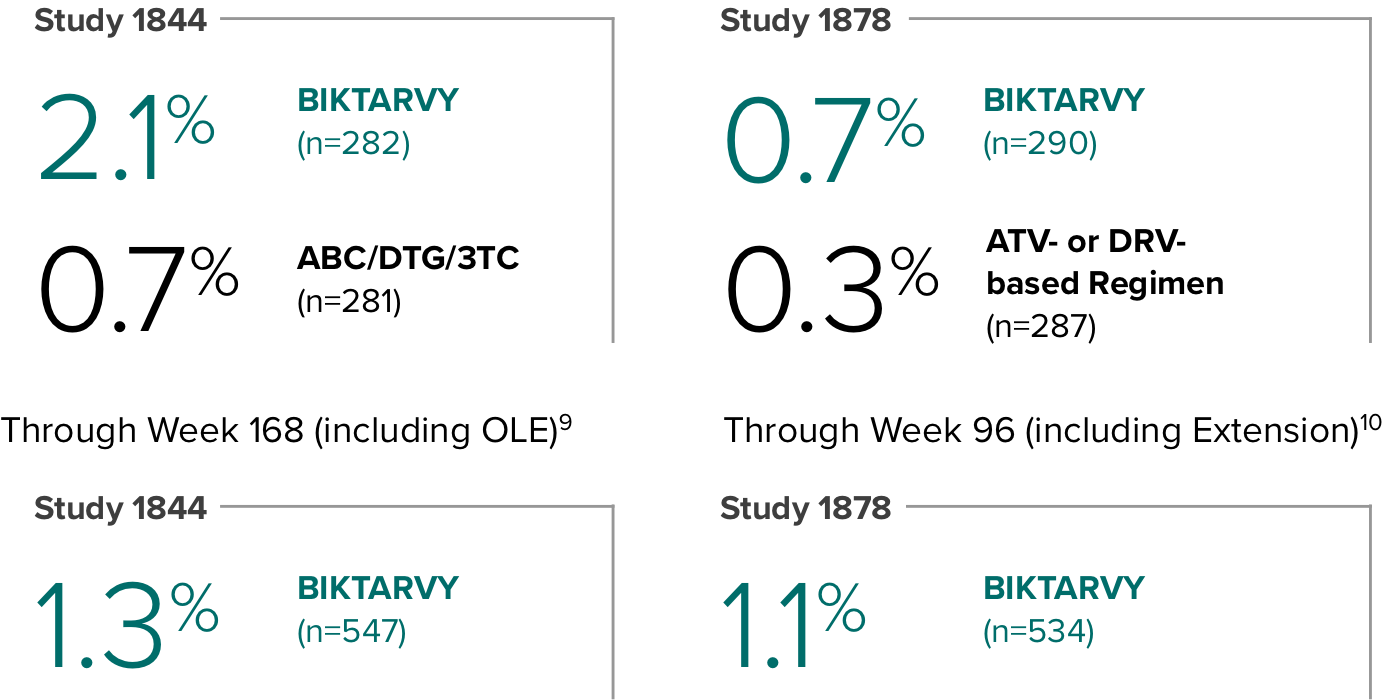
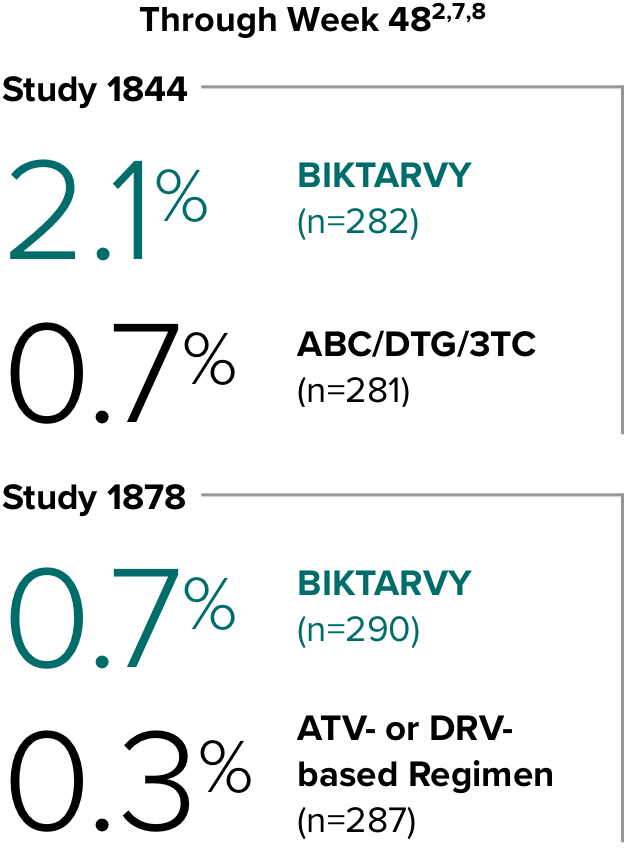
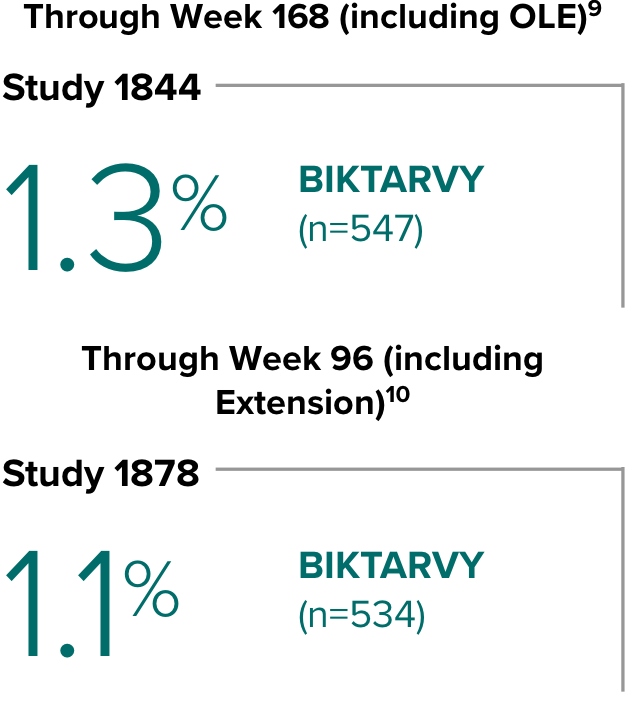
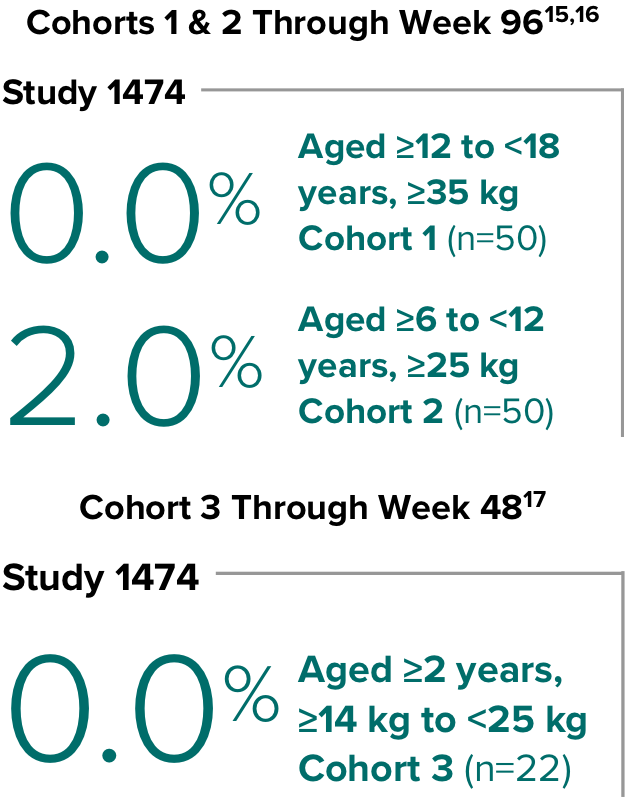
Weight change through Week 481
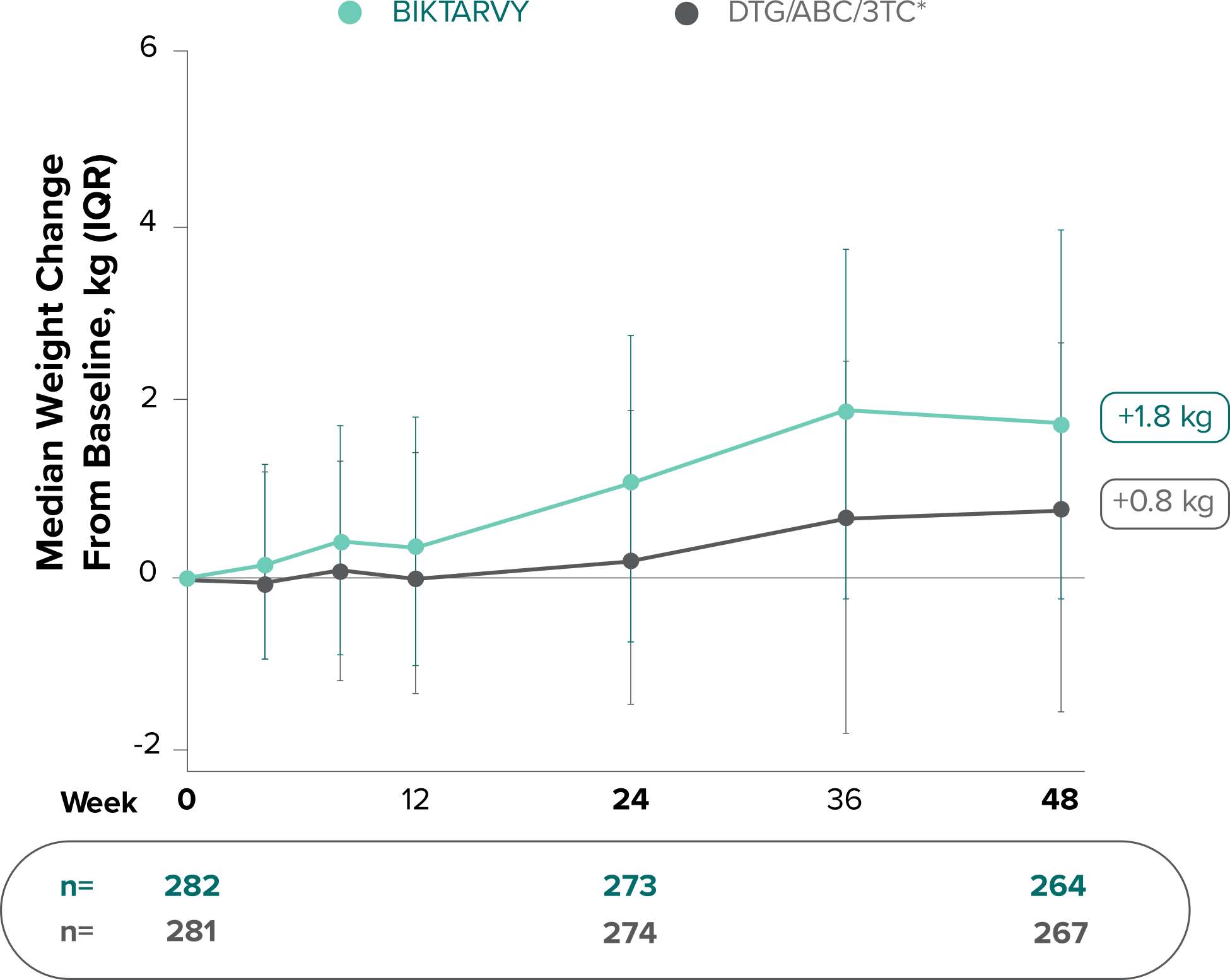
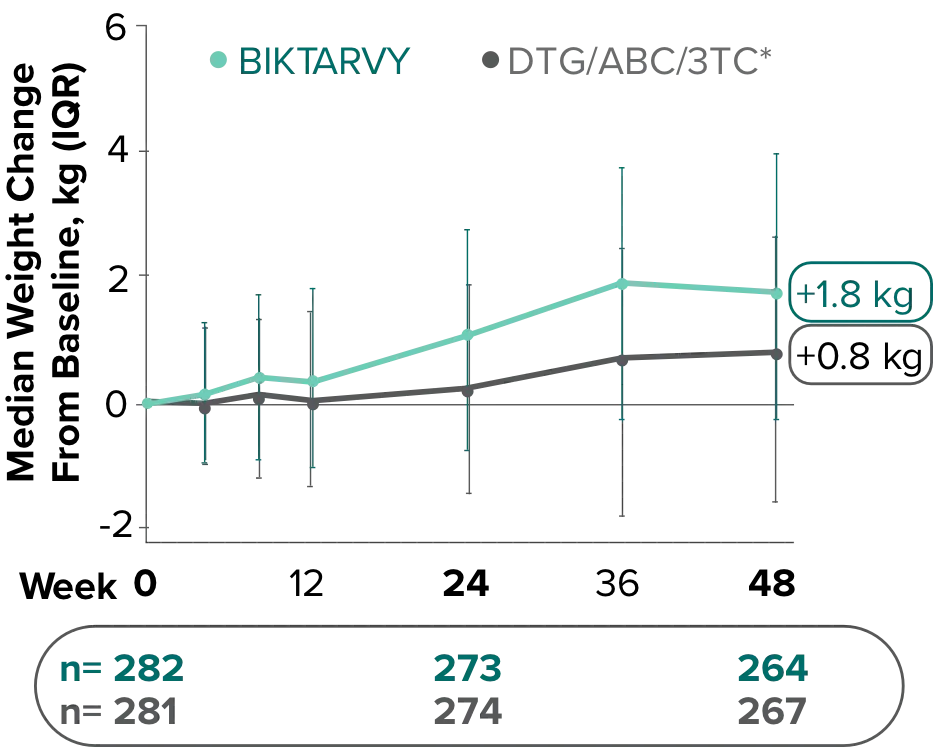
Weight change through Week 1201,†,‡
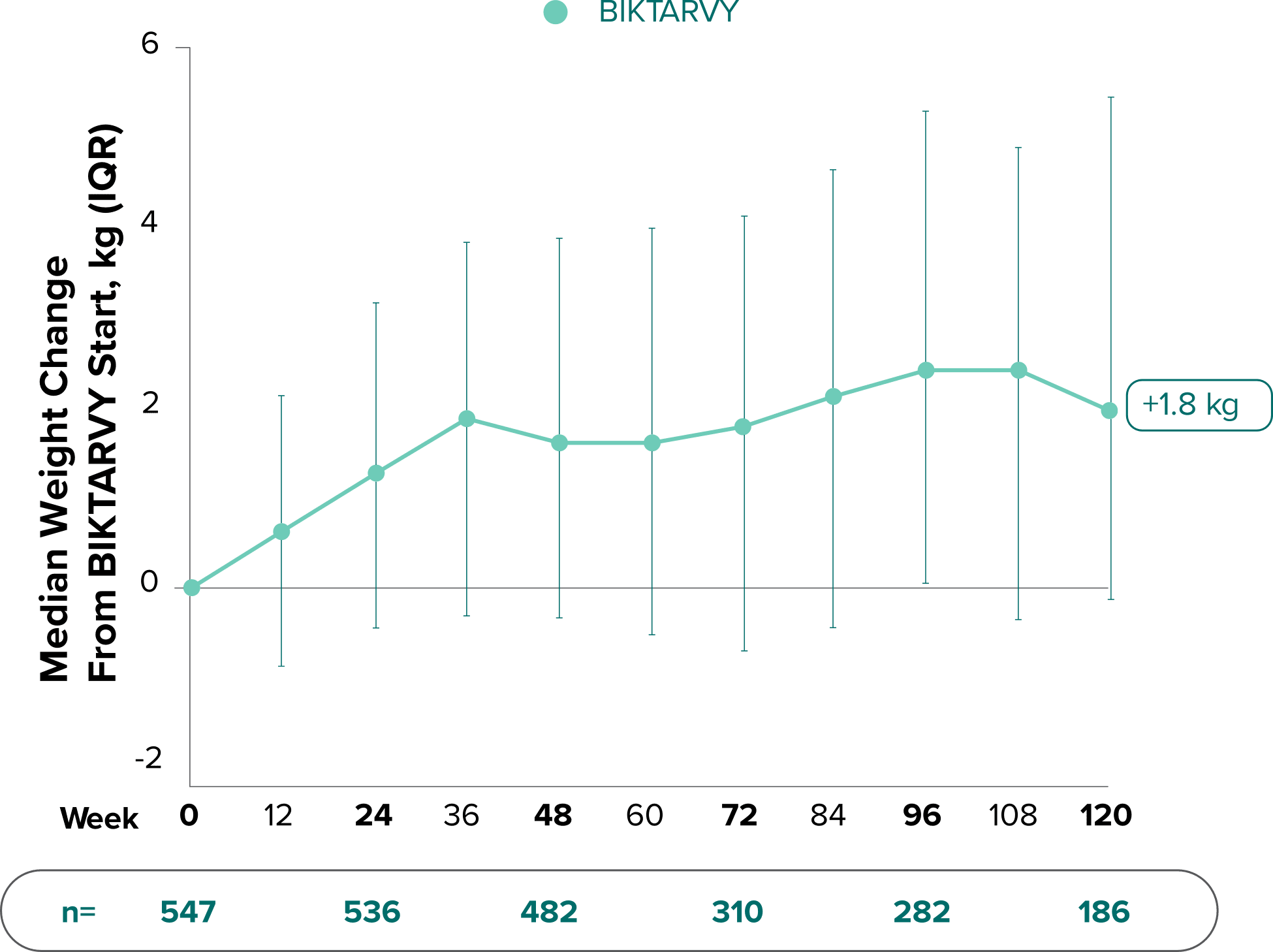
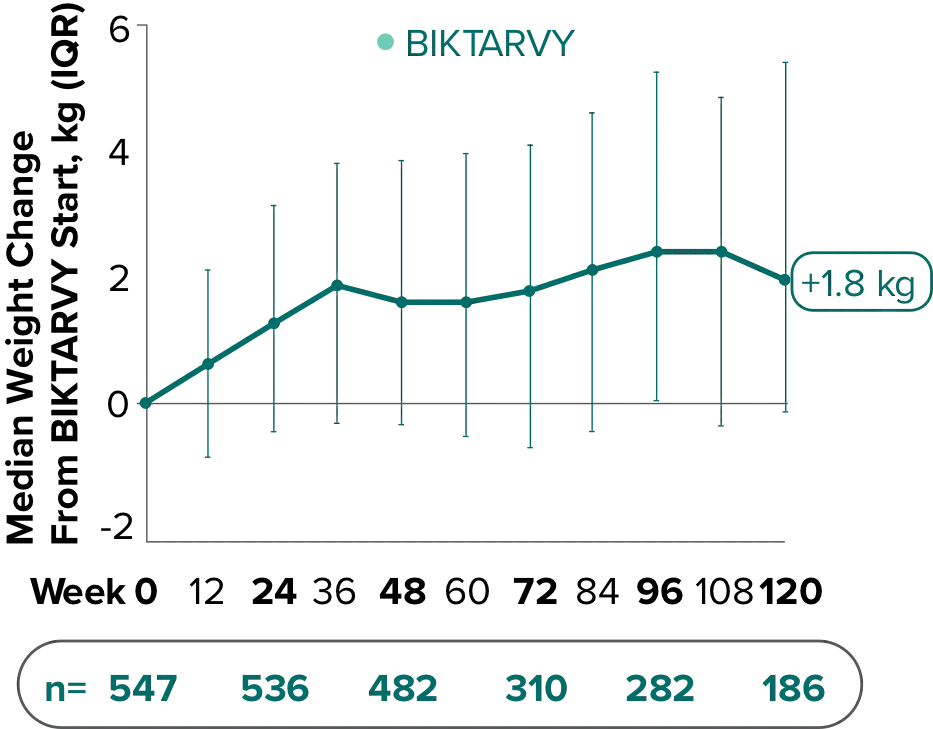
In Study 1844, no adults discontinued BIKTARVY due to weight-related adverse events through Week 1681,2
- In participants who continued on or switched to BIKTARVY during OLE, changes from baseline in body weight were consistent with changes reported through Week 481
*Shown for reference.
†Low participant numbers out to Week 168 (n=12); median change at Week 168: +2.1 kg.
‡This analysis includes participants initially randomized to BIKTARVY and participants who switched to BIKTARVY during the OLE.
3TC, lamivudine; ABC, abacavir; DTG, dolutegravir; IQR, interquartile range; OLE, open-label extension.
References:
- Brar I, Ruane P, Ward D, et al. Long-term follow-up after a switch to bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide from dolutegravir, abacavir, and lamivudine. Poster presented at: IDWeek; October 21-25, 2020; Virtual. Poster 1028.
- Molina J-M, Ward D, Brar I, et al. Switching to fixed-dose bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide from dolutegravir plus abacavir and lamivudine in virologically suppressed adults with HIV-1: 48 week results of a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, active-controlled, Phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet HIV. 2018;5(7):e357-e365.
Weight change through Week 481,2
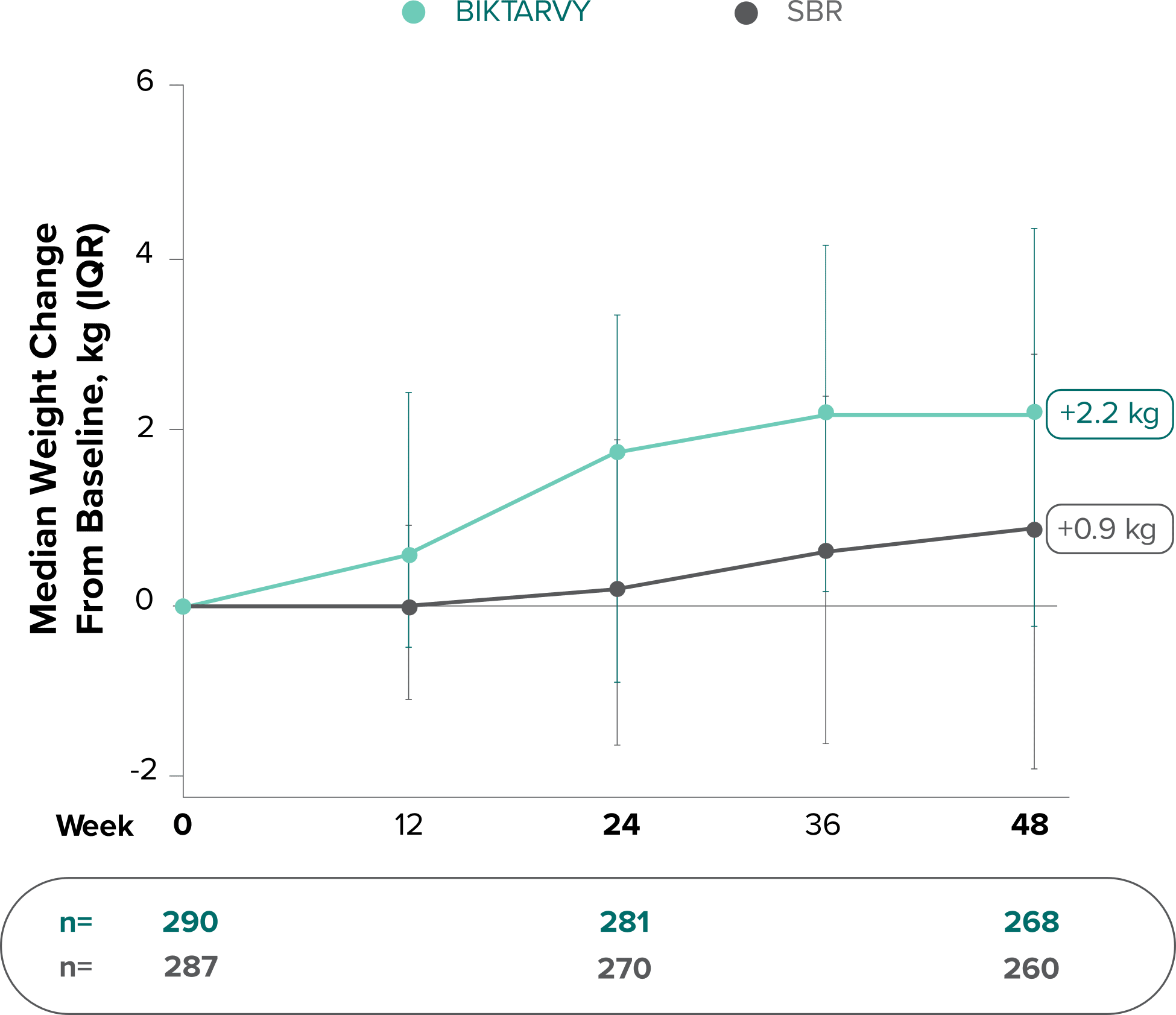
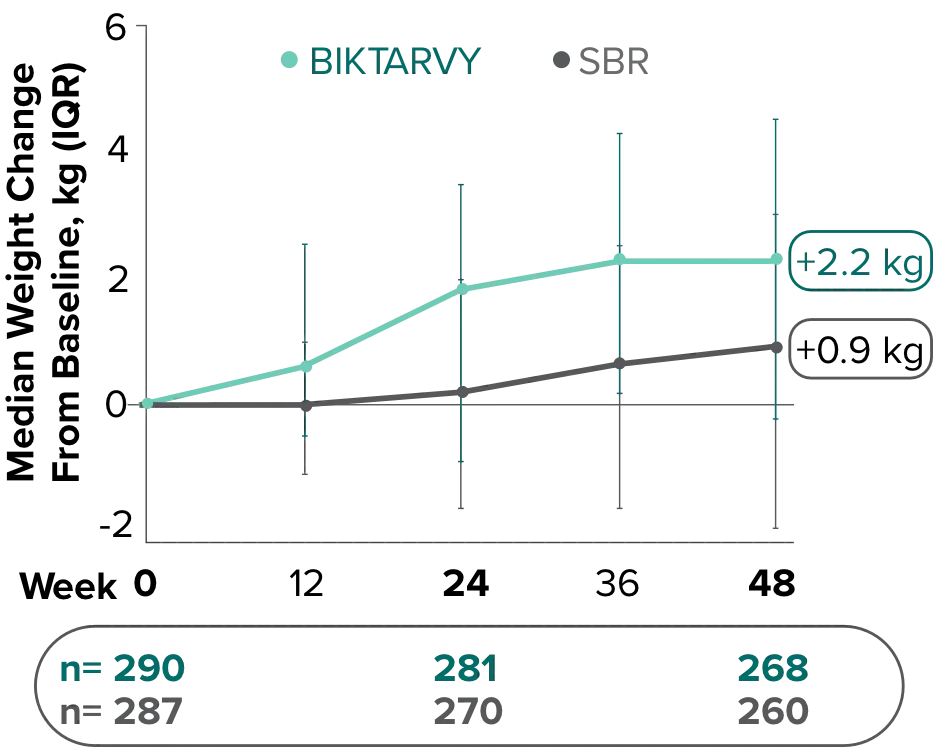
Weight change through Week 961,*
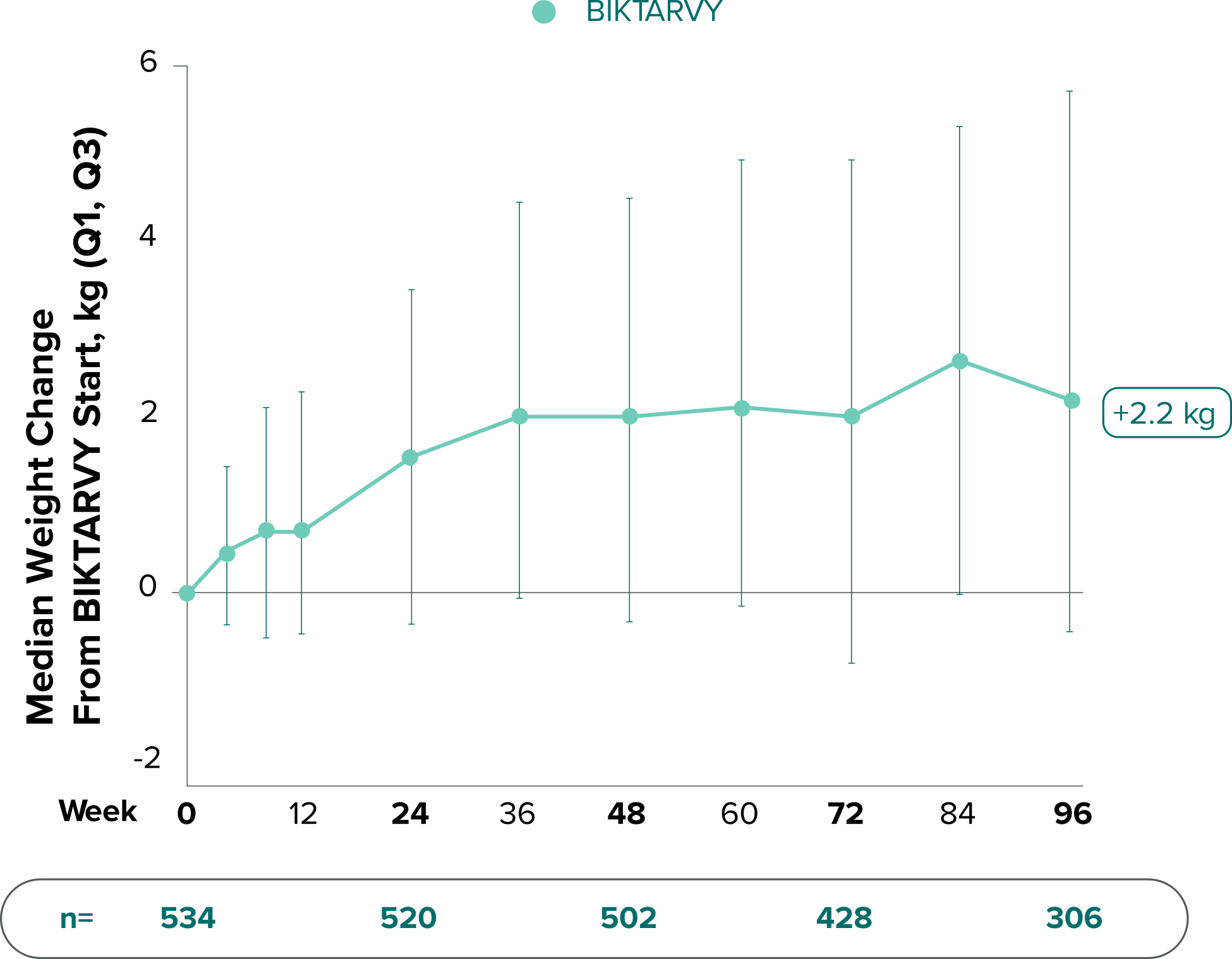
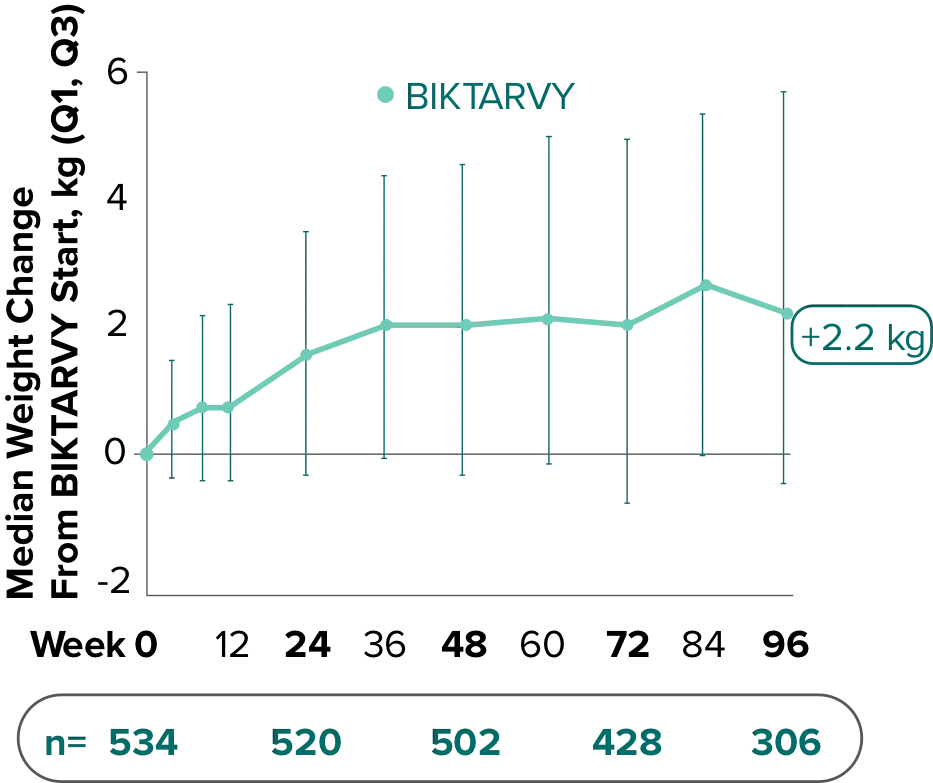
In Study 1878, no adults discontinued BIKTARVY due to weight-related adverse events through Week 961,3
- In participants who continued on or switched to BIKTARVY during the extension phase, changes from baseline in body weight were consistent with changes reported through Week 481
*This analysis includes participants initially randomized to BIKTARVY and participants who switched to BIKTARVY during the extension phase.
IQR, interquartile range; SBR, stayed on baseline regimen.
References:
- Rockstroh J, Molina J-M, Post F, et al. Long-term follow-up after a switch to bictegravir, emtricitabine, tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF) from a boosted protease inhibitor-based regimen. Poster presented at: HIV Drug Therapy Glasgow 2020; October 5-8, 2020; Virtual. Poster P036.
- Data on file. Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Daar ES, DeJesus E, Ruane P, et al. Efficacy and safety of switching to fixed-dose bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide from boosted protease inhibitor-based regimens in virologically suppressed adults with HIV-1: 48 week results of a randomised, open-label, multicentre, Phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet HIV. 2018;5(7):e347-e356.
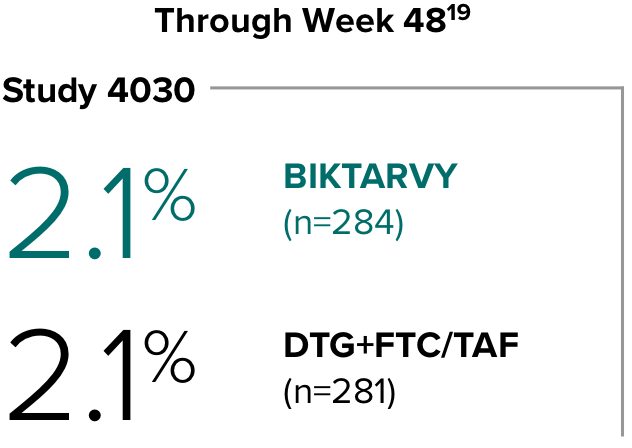
Weight change from baseline through Week 481
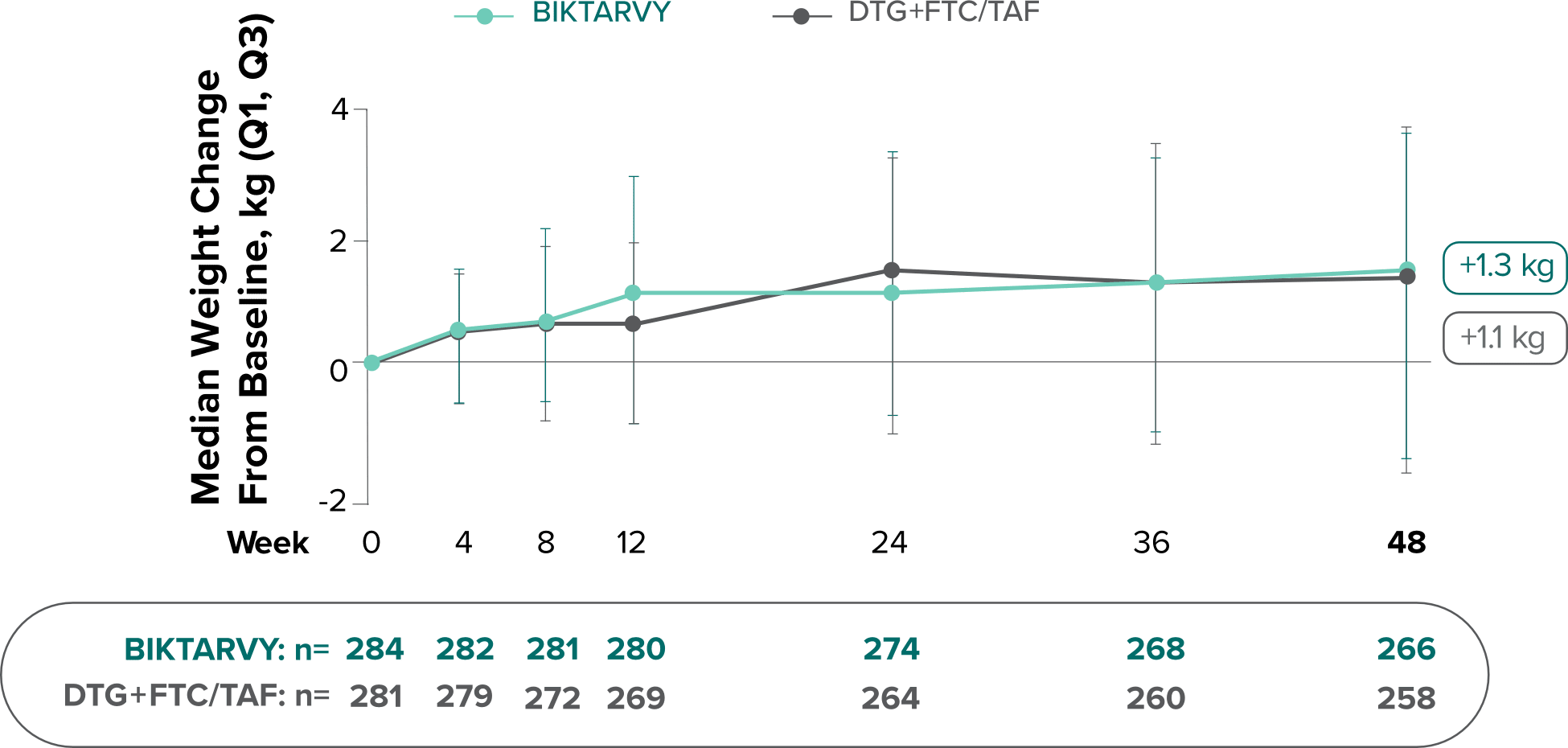
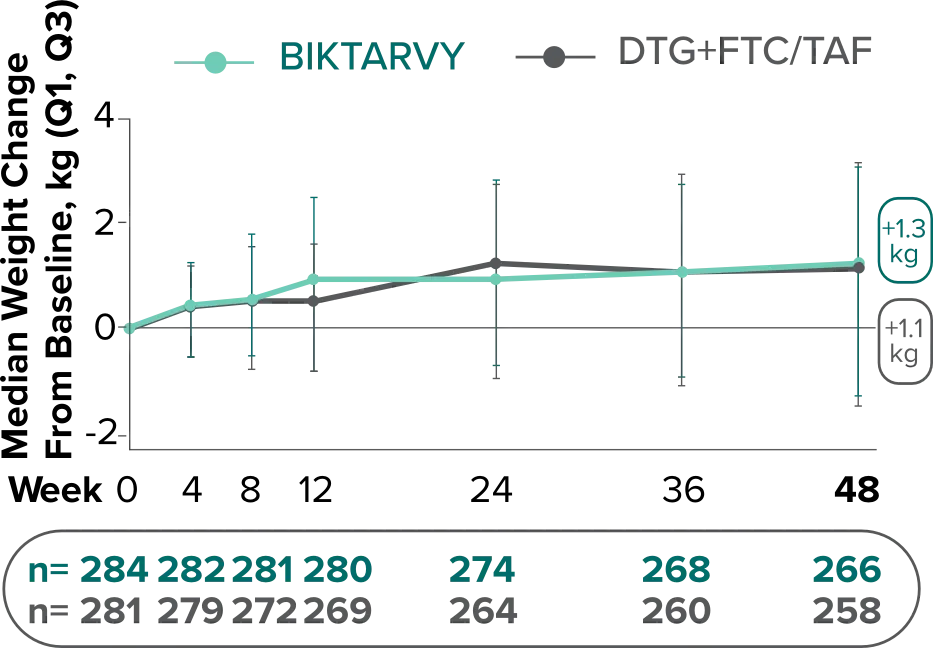
Weight changes were similar through Week 48 (P = 0.46) in adults who were randomized to BIKTARVY and those who were randomized to DTG+FTC/TAF. In Study 4030, significantly more weight gain was observed at Week 48 (P < 0.001) in participants switching from TDF-based regimens (+2.2 kg) compared with those remaining on TAF-based regimens (+0.6 kg).2
References:
- Data on file. Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Sax PE, Rockstroh JK, Luetkemeyer AF, et al; GS-US-380-4030 Investigators. Switching to bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide in virologically suppressed adults with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;73 2):e485-e493.
Changes in eGFRCG through Week 481
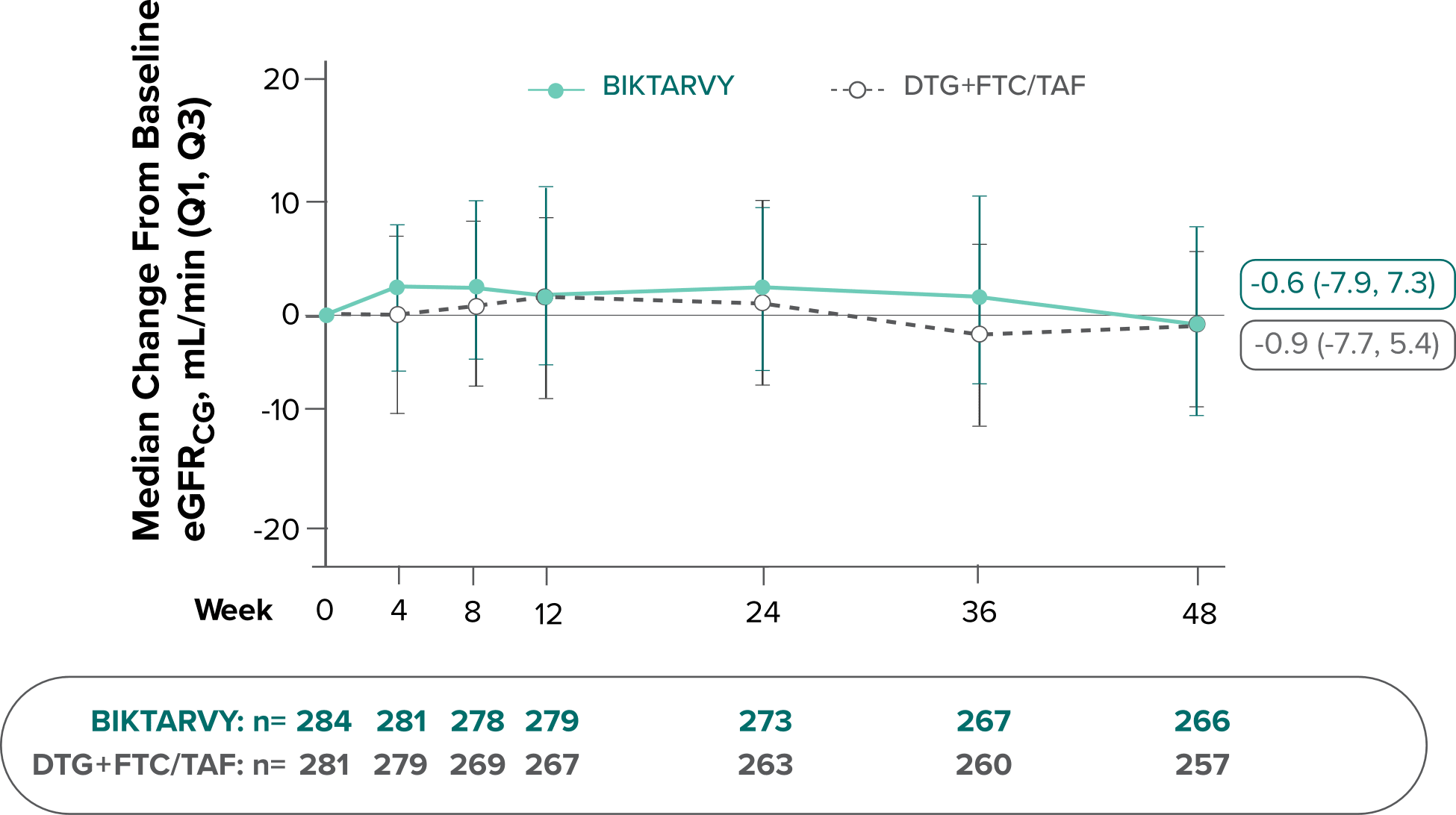
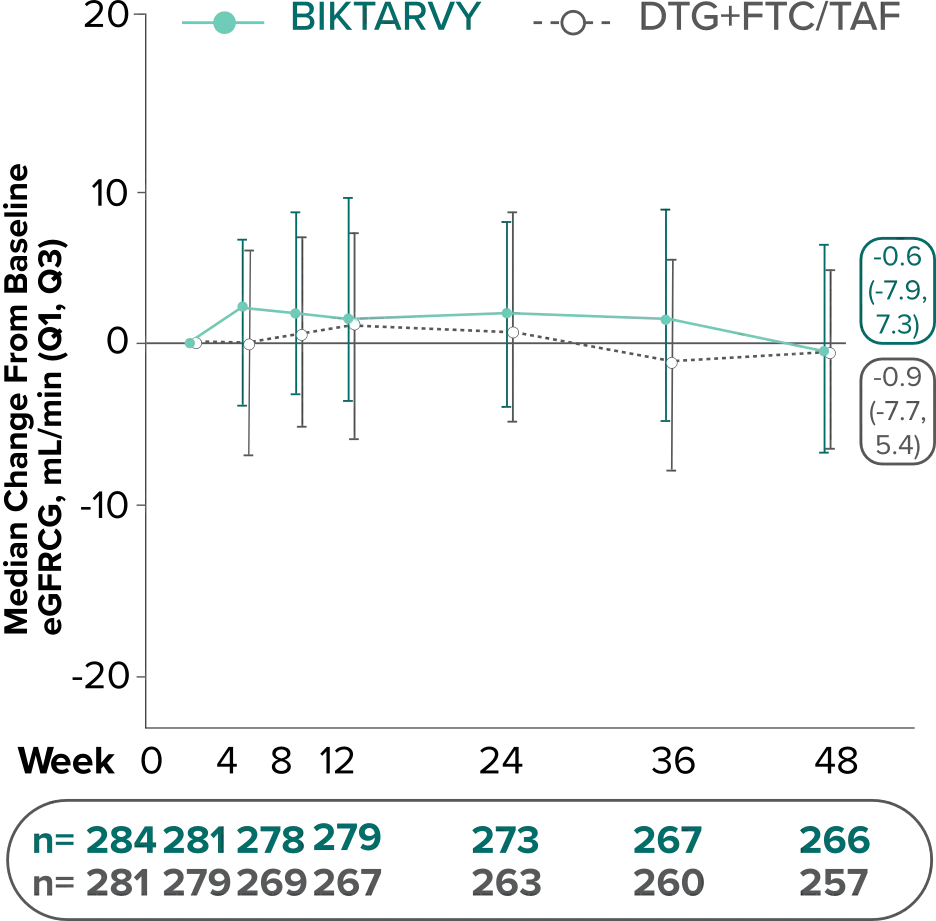
In Study 4030, median changes from baseline in eGFR were similar between groups at Week 48 (P=0.38).
There were no discontinuations due to renal-related adverse events and no cases of proximal renal tubulopathy.2
The long-term clinical significance of changes in eGFR is not known.
- BIKTARVY is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). For patients weighing ≥25 kg, BIKTARVY is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (estimated CrCl <30 mL/min) except in virologically suppressed patients with CrCl <15 mL/min on chronic hemodialysis. BIKTARVY is not recommended for patients weighing ≥14 kg to <25 kg with CrCl <30 mL/min.3
References:
- Data on file. Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Sax PE, Rockstroh JK, Luetkemeyer AF, et al; GS-US-380-4030 Investigators. Switching to bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide in virologically suppressed adults with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;73(2):e485-e493.
- BIKTARVY. Prescribing information. Gilead Sciences, Inc.; 2025.
Median changes in fasting lipids from baseline through Week 481
Study 4030
BIKTARVYBaseline (n=280)Week 48 (n=252)
DTG+FTC/TAFBaseline
(n=278)Week 48
(n=249)
Total cholesterol (mg/dL)
-1
-1
Direct LDL (mg/dL)
3
4
HDL (mg/dL)
0
1
Total cholesterol to HDL ratio
-0.1
0.0
Triglycerides (mg/dL)
1
0
Lab abnormalities were observed with both BIKTARVY and comparators through Week 481
Study 4030
Reported in ≥2% (Grades 3-4) of Participants in Either Group
BIKTARVY
(n=284)
DTG+FTC/TAF(n=281)
Amylase (increased)
2%
3%
Creatine kinase (increased)
4%
2%
LDL (fasting increased)
5%
3%
Lipase (increased)*
17%
20%
Glycosuria†
2%
3%
*Lipase test performed only in participants with serum amylase >1.5 x ULN.
†Glycosuria abnormalities were all reported in the setting of hyperglycemia.
References:
- Sax PE, Rockstroh JK, Luetkemeyer AF, et al; GS-US-380-4030 Investigators. Switching to bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide in virologically suppressed adults with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;73(2):e485-e493.
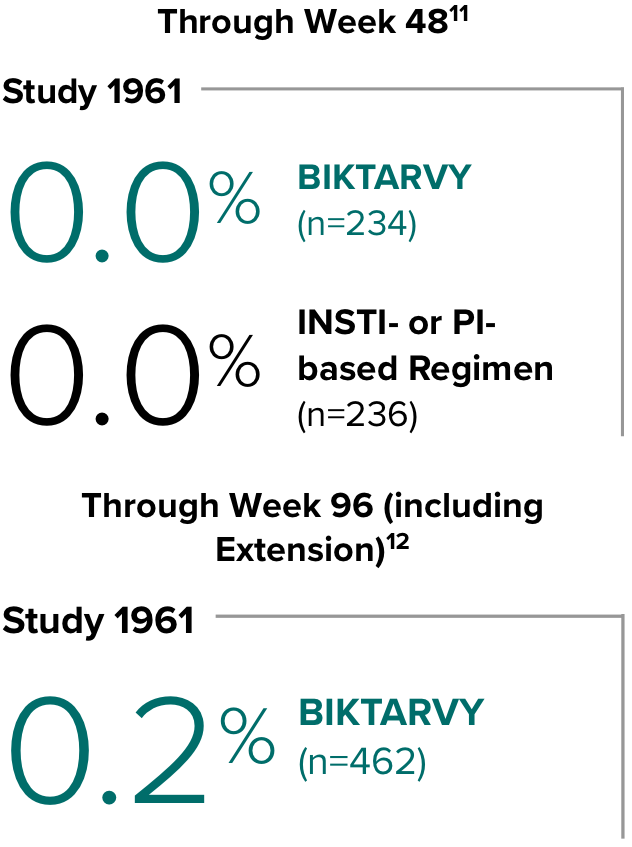
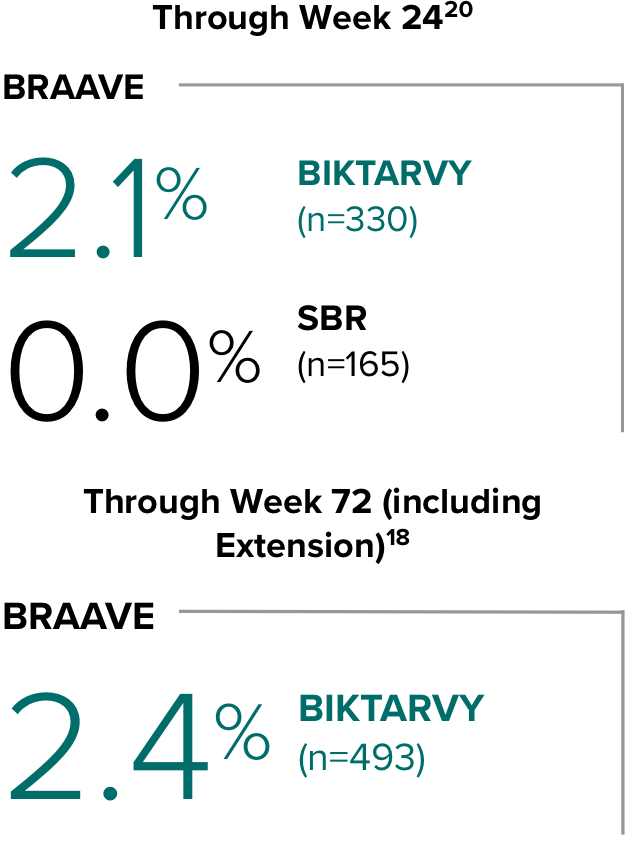
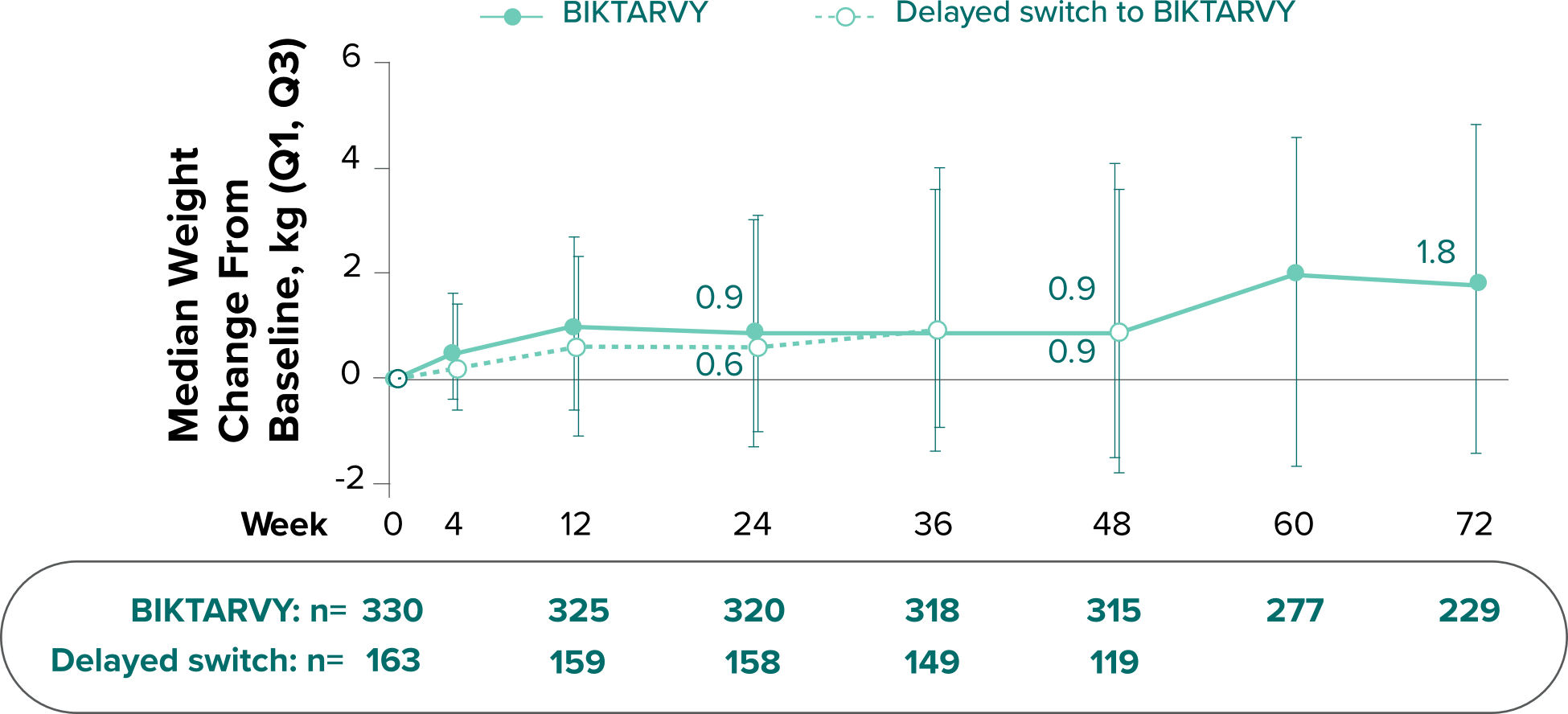
Weight change from baseline through Week 721-3
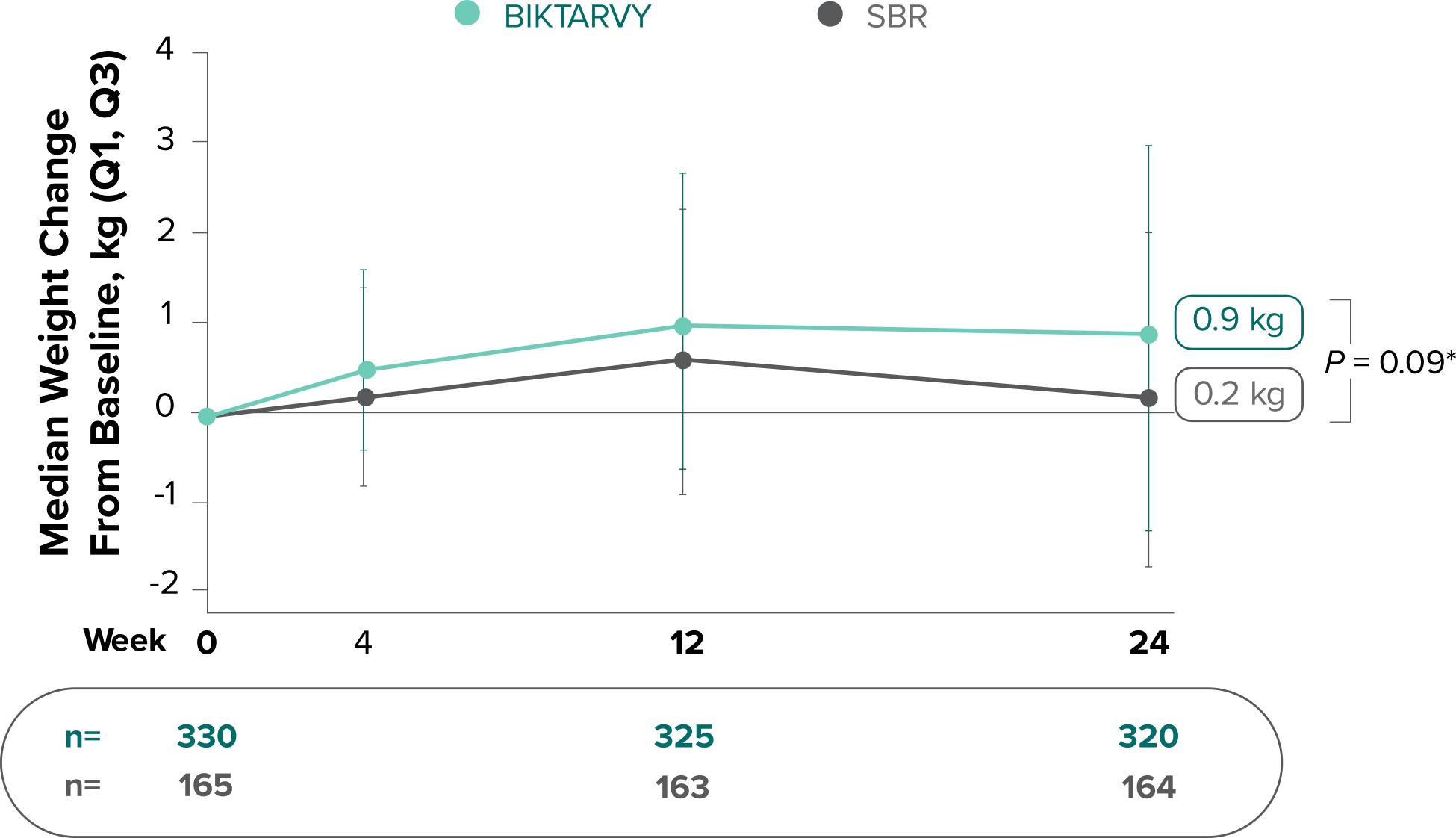
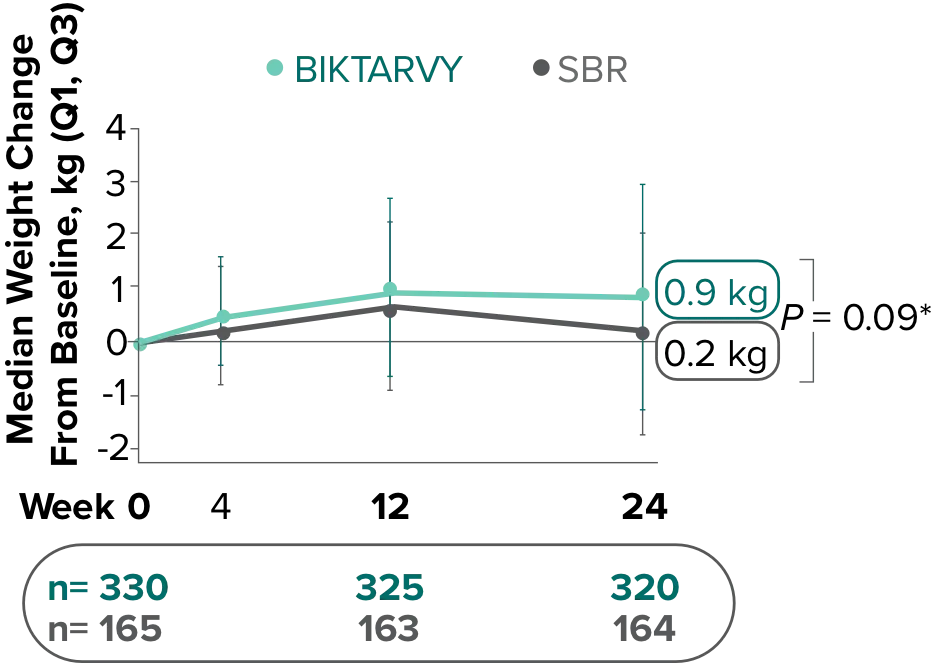
Weight Change Through Week 24
Weight Change Through Week 72
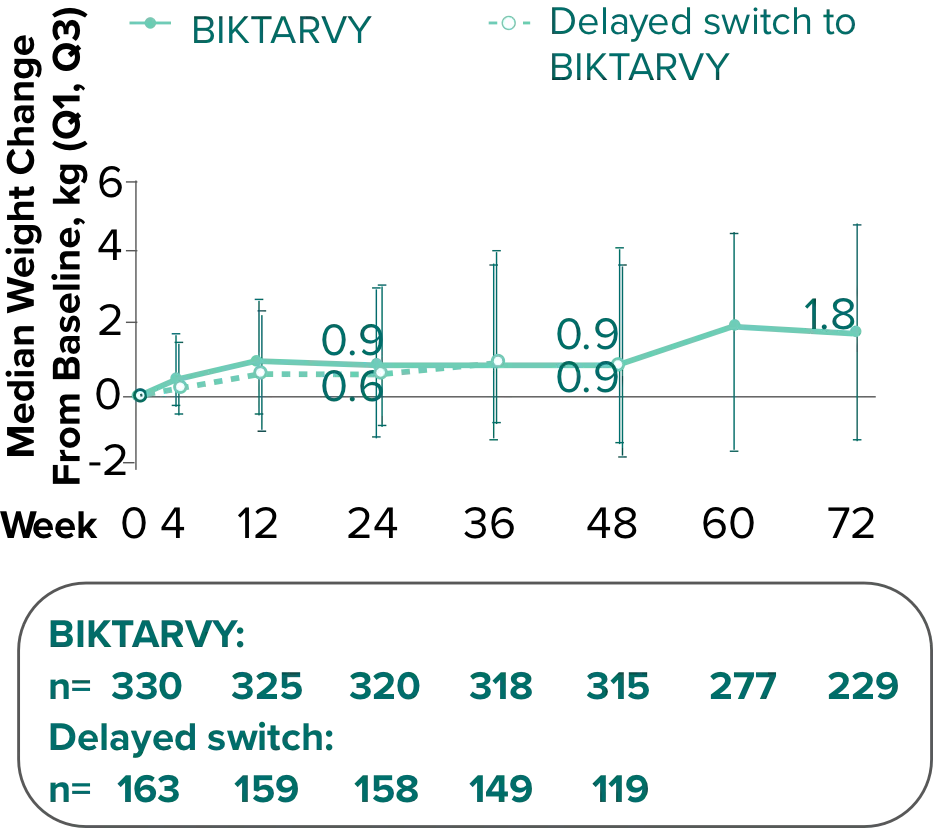
Weight changes through Week 24 were similar between adults who were randomized to BIKTARVY and those who stayed on baseline regimen1-3
In BRAAVE, no adults discontinued due to weight-related adverse events through Week 723
*From 2-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test comparing BIKTARVY vs SBR at Week 24.
SBR, stayed on baseline regimen.
References:
- Hagins D, Kumar P, Saag M, et al. Switching to bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide in Black Americans with HIV-1: a randomized Phase 3b, multicenter, open-label study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2021;88(1):86-95
- Hagins DP, Kumar PN, Saag M, et al. Randomized switch to B/F/TAF in African American adults with HIV. Abstract presented at: Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; March 8-11, 2020; Boston, MA. Abstract 36.
- Kumar P, Stephens JL, Wurapa AK, et al. Week 72 outcomes and COVID-19 impact from the BRAAVE 2020 study: a randomized switch to B/F/TAF in Black American adults with HIV. Poster presented at: International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science; July 18-21, 2021; Virtual. Poster PEB161.
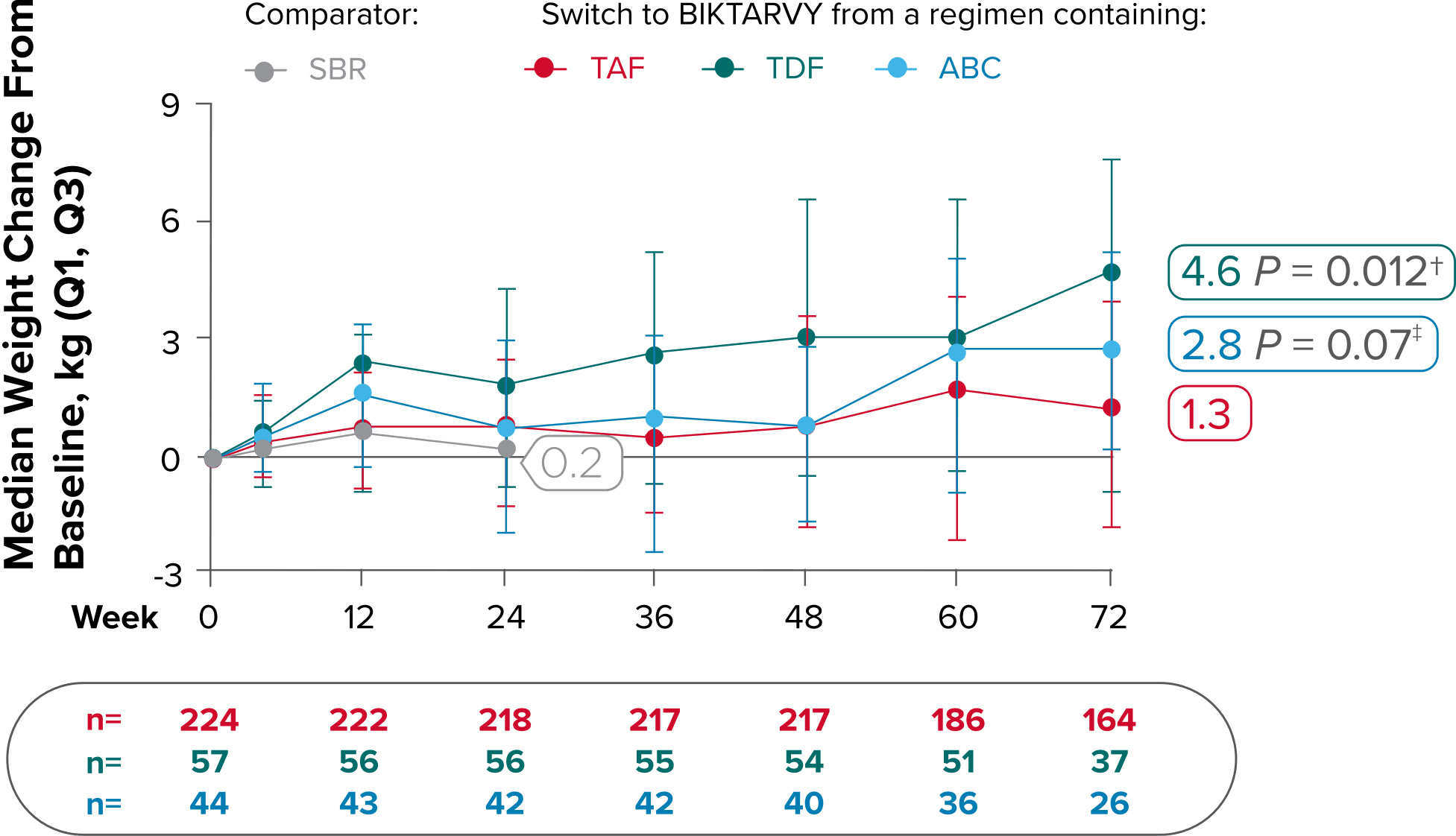
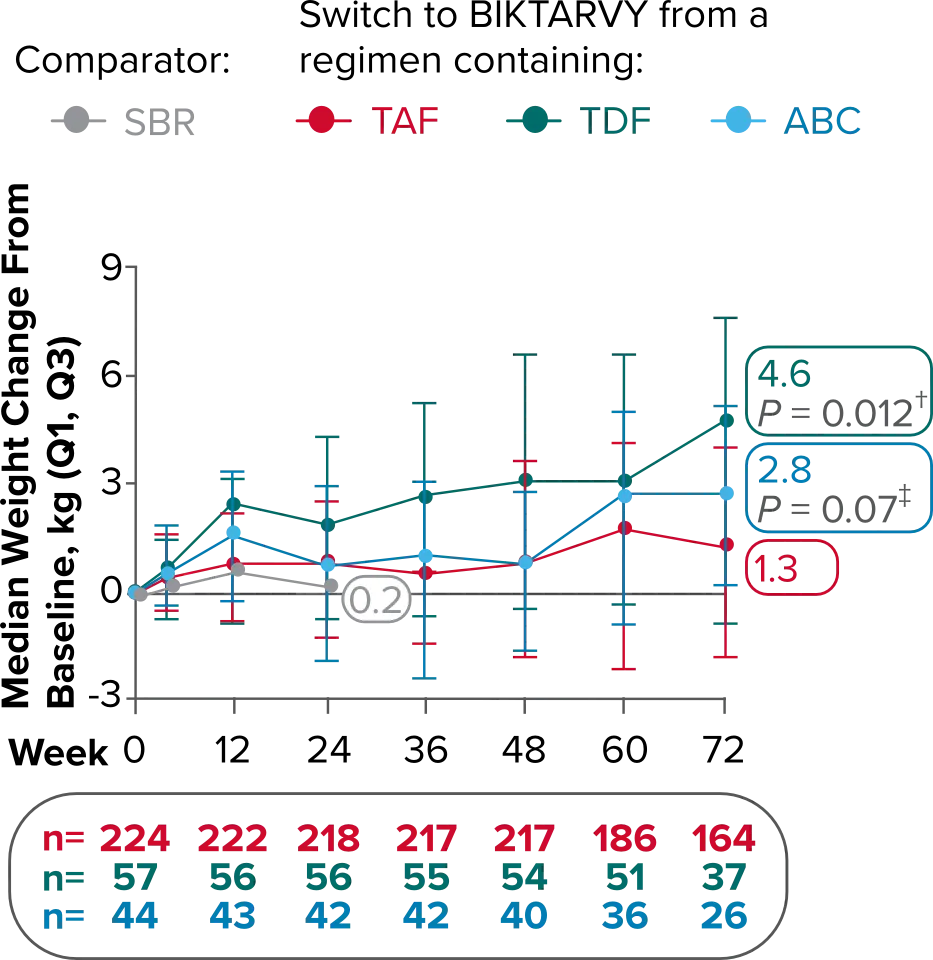
Weight changes through Week 721
SBR vs BIKTARVY
Delayed Switch*
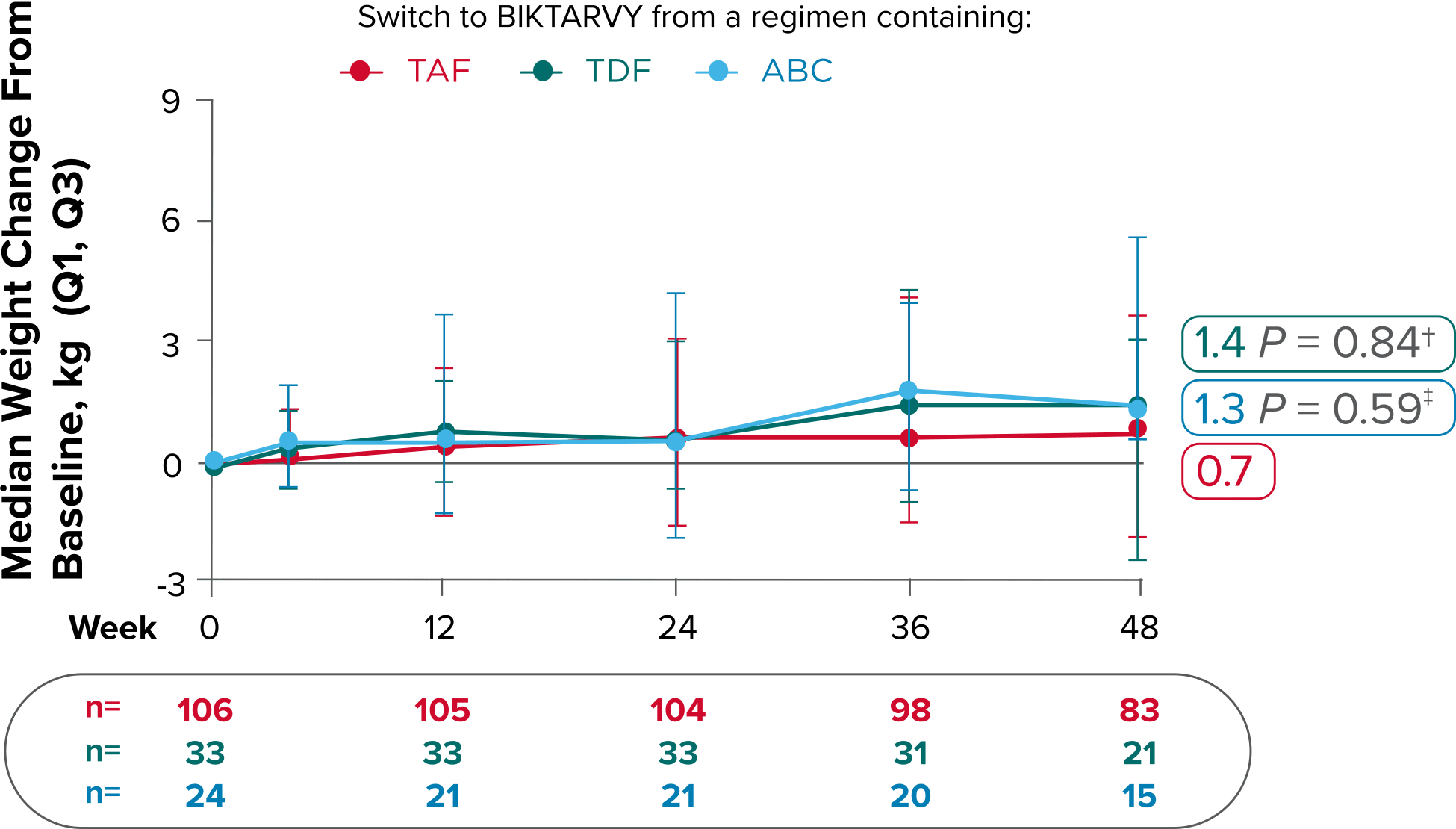
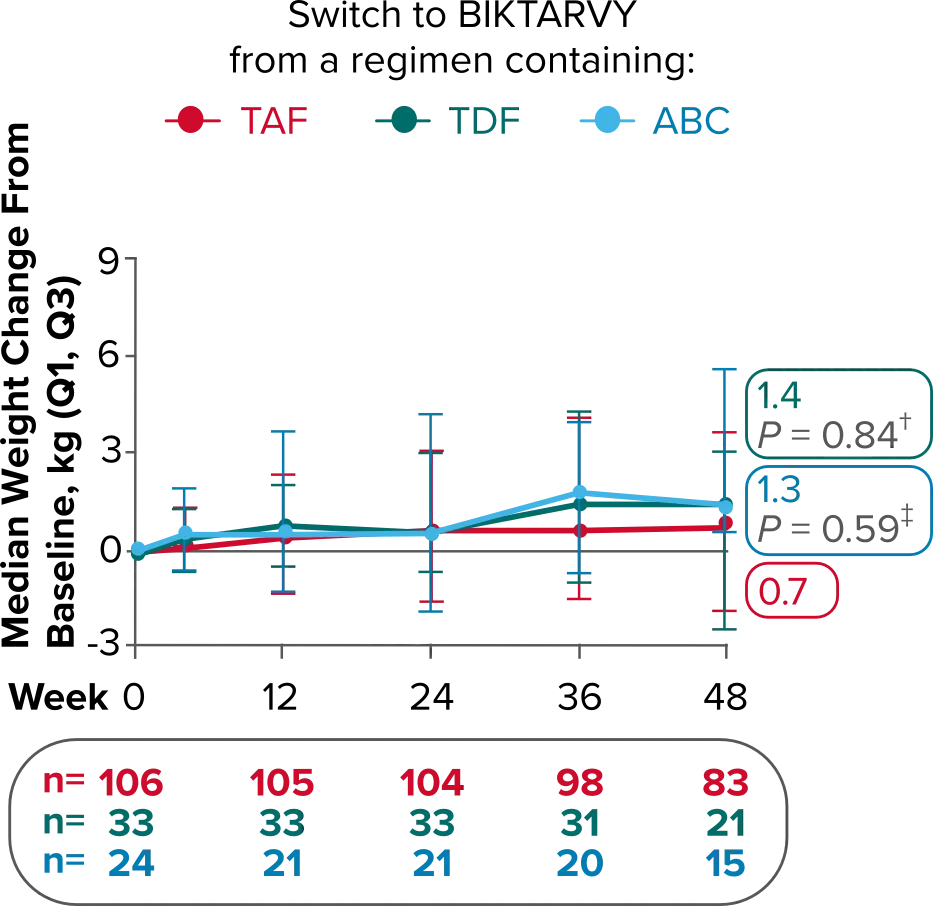
More weight gain was observed at Week 72 in participants switching from TDF- or ABC-based regimens compared with those remaining on a TAF-based regimen1
*Baseline for delayed switch: time of first BIKTARVY dose.
†From 2-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test comparing baseline regimens containing TAF vs TDF.
‡Comparing baseline regimens containing TAF vs ABC.
ABC, abacavir; NRTI, nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; SBR, stayed on baseline regimen; TAF, tenofovir alafenamide; TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
Reference:
- Kumar P, Stephens JL, Wurapa AK, et al. Week 72 outcomes and COVID-19 impact from the BRAAVE 2020 study: a randomized switch to B/F/TAF in Black American adults with HIV. Poster presented at: International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science; July 18-21, 2021; Virtual. Poster PEB161.